The power supply unit (PSU) is an important component for a desktop PC, but not everyone prioritizes it when building a PC. It delivers stable and efficient power to all other connected components like motherboard, CPU, GPU, storage drives, and more. If you’re also looking for a compatible power supply, you can choose the right PSU for your PC to ensure reliable performance and component safety.
Finding a ‘compatible’ power supply unit for your computer can be difficult for some people who building their desktop PC for the first time. But compatibility is only one of the things of importance here. You should also consider other aspects like power rating, efficiency, design preferences, and budgetary restrictions. To help you navigate all these, here’s a complete guide on how to choose the right PSU for your PC.
What is a PSU?

A PSU (Power Supply Unit) is an electronic hardware component that is used in desktop PCs to convert the main AC (alternating current) power to the DC (direct current) power. It’s useful for PC components like motherboards, processors, graphics cards, storage devices, and other peripherals to run properly.
In short, the PSU distributes the electricity to major PC components and stabilizes power surges or spikes so that other components won’t get damaged. You can say that the power supply unit works as a central power hub for your complete PC hardware. For laptops, you don’t have to think about choosing a compatible power adapter because the manufacturer provides it in of the box.
However, that’s not the case with desktop PCs. To run a desktop computer such as a gaming PC or a workstation, you need an external power supply unit to buy and connect to the motherboard. Without having a power supply component, you won’t be able to power other PC components directly.
Importance of a Power Supply Unit
The power supply unit is a crucial part of any computer, but we usually don’t give enough attention to it. Instead, we focus on other components and aesthetic parts. Though entry-level PC users can go with any basic power supply, overlooking the importance of a PSU in a high-performance build can lead to unexpected issues like damaging any component or blowing up the whole PC.
As you can understand from the name, a power supply unit distributes power to your whole desktop, and choosing the wrong or underpowered PSU can cause the worst consequences. If you have a modern PC build and the specs are pretty powerful, it’s always a better idea to get a compatible power supply. Otherwise, things could go haywire if the power supply isn’t sufficient during a considerable load.
Power surges and voltage fluctuations are pretty common across the world, even in this 21st century. Meanwhile, plenty of cities and villages are still facing power outages and occasional power-offs randomly. Such situations can badly impact your PC while running. Any kind of electrical hazard can take place unexpectedly. However, a certified compatible power supply can prevent such issues.
Therefore, if your PC is randomly shut down or running into booting issues, you should carefully troubleshoot your PSU. Mostly, replacing the PSU can fix such issues immediately.
What to Consider When Buying a PSU
You should research the PSU, depending on your budget and PC configuration, to determine what kind of power supply you require. You need to consider everything from the wattage to form factor to efficiency rating before buying a new PSU. Here, we’ve provided all the basic information of a PSU below that you should know while picking up:
1. Check for PSU Wattage
The first step is to calculate how much power output your PC build will require overall during full load. If you want to understand things better, we’ve listed an overview below of how much power your PC components may typically consume:
| PC Components | Power Consumption (wattage) |
| Processor: Top-tier like Intel Core i7/i9 or AMD Ryzen 7/9 | Maximum 150 watts |
| GPU: Nvidia RTX 3080/4090 or AMD RX 6900XT/7900XTX | Maximum 350 watts |
| Other Components: Motherboard, PCIe cards, storage, RAM, etc | Maximum 100 watts |
| Additional: Consumption for efficiency and future upgrades | Maximum up to 20%-30% of extra |
- 1,000W+: It’s required to be on the safe side for high-end PC specs like Intel Core i9 or AMD Ryzen 9 and Nvidia GeForce RTX 4090 or AMD Radeon RX 7900 XTX.
- 800W: If you’re using Intel Core i7 or AMD Ryzen 7 and Nvidia GeForce RTX 4080 or AMD Radeon RX 7800 XT specs.
- 600W: This is the standard PSU wattage you should consider for most mid-ranger modern PC specs like Intel Core i5 or AMD Ryzen 5 and Nvidia GeForce RTX 3060/4060, AMD Radeon RX 7600, or Intel Arc A750.
- 400W-450W: This power supply can be sufficient for entry-level PC specs like Intel Core i3 or AMD Ryzen 3 and Nvidia GTX 1650 or AMD RX570. Even if you don’t require an external graphics card, a 400W PSU is all you need.
Alternatively, you can also try online PSU wattage calculators like Cooler Master Power Supply Calculator or MSI Power Supply Calculator to determine the ideal power requirements easily.
To do so, simply select the PC component models that you plan to use for every category, such as a CPU model, motherboard model, GPU model, RAM, storage, etc. Then, the calculator tool will check the approximate wattage requirement of the PSU. It’ll ensure you choose a PSU with a similar wattage to get optimal performance and stability.
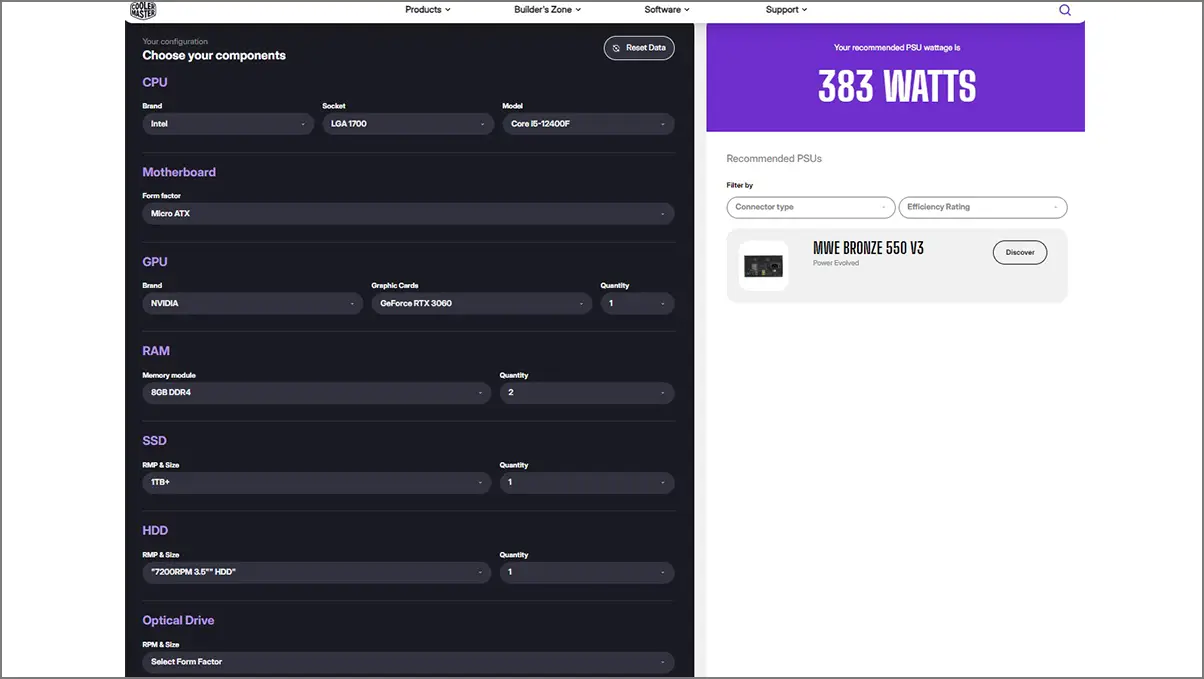
For example, if you’re planning to buy PC components like an Intel Core i5-12400F CPU, an Nvidia RTX 3060 GPU, 16GB (2x8GB) of DDR4 RAM kit, a 1TB M.2 NVME SSD, and a 1TB 7200RPM HDD, then the recommended PSU wattage will be around 400 watts. For that scenario, the calculator tool will recommend you go with an 80+ Bronze certified 550W PSU. But we suggest you buy a 650W PSU to be safe and future-proof. The same thing will be applied for lower or higher PSU wattage.
2. PSU Form Factor
The form factor also plays a vital role in your PC case. If your power supply unit is big, it won’t fit properly in the case. So, selecting the right PC case is also necessary to accommodate the PSU accordingly. If you’ve already purchased a specific PC case or decided to get one, choose a PSU form factor that can match the measurements.
Fortunately, most PSUs come in the ATX form factor, which means mid-tower and full-tower PC cases will easily fit. Still, you should cross-check the form factor before purchasing. On the other hand, small form factor PC cases should be compatible with a smaller PSU. Keep in mind that bulky graphics cards like Nvidia RTX 4090 or AMD Radeon RX 7900 XTX with multiple SSDs inside the PC case can cause issues with the space for a PSU.
So, it all depends on the form factor of a PC case because of the set of standardized dimensions. Here, we’ve mentioned all the PSU form factors below that can help you choose the right one for your PC case:
- ATX: This is the most common form factor of PSUs – ATX PS/2 (150 mm x 86 mm x 140 mm), which can easily fit into most PC cases with additional cooling options on most mid-tower and full-tower cases. It offers a single 20-pin connector as the primary connector.
- ATX12V: It has become mainstream in recent years, better than ATX. However, the form factor is identical to the specs of ATX12V 2.1 and ATX12V 2.2.
- SFX: It’s a small and compact form factor applicable for Mini-ITX PC cases. SFX PSUs typically measure 125 mm x 63.5 mm x 100 mm.
- SFX-L: It has a slightly larger form factor than SFX, with a measure of 125 mm x 63.5 mm x 125 mm.
- TFX: Here, TFX indicates (Thin Form Factor eXtended) PSU form factor that works with slim or low-profile PC cases, offering low wattage and basic connectivity, such as home media PCs or ultra-slim desktops.
- CFX: It usually means Compact Form Factor PSU, which is designed for small form factor machines. CFX PSUs are compatible with a total system volume of 10-15 liters, ranging from 220W-300W power supply.
- EPS12V: The EPS12V PSU form factor uses an 8-pin EPS connector with a 4-pin ATX12V connector. Initially, it was designed for entry-level servers but ended up with high-end desktop PCs for the 8-pin EPS12V connector. It allows users to go with an EPS12V PSU.

3. Efficiency Rating (80 PLUS Certification)
All PSUs come with power load efficiency ratings, denoted by 80 PLUS Certification. It indicates how well a power supply unit is capable of delivering power efficiency. So, higher efficiency means better load stability. As no power supply is 100% efficient, you should always consider maximum efficiency in 50% load.
With higher efficiency, your PSU will consume less power, which means less heating and less pressure to work. It will lead to a longer lifespan of the PSU and an almost quiet fan spinning for silent usage. However, the more efficient PSU is costly enough if your budget is limited.
For instance, a 1,000W PSU can deliver up to 900W to PC components, which is precisely 90% efficient. Similarly, a better power supply unit is capable of delivering up to 800W out of a 1,000W capacity, which is precisely 80% efficient.
So, while purchasing a PSU for a mid-budget or high-end PC build, you should consider 80 Plus certification. This means that the PSU is guaranteed to deliver at least 80% efficiency while running at 10%, 20%, 50%, and 100% load capacity. You can check out the common efficiency ratings below:
| PSU 80 Plus Certified | 10% Load | 20% Load | 50% Load | 100% Load |
| 80 Plus | – | 80% | 80% | 80% |
| 80 Plus Bronze | – | 82% | 85% | 82% |
| 80 Plus Silver | – | 85% | 88% | 85% |
| 80 Plus Gold | – | 87% | 90% | 87% |
| 80 Plus Platinum | – | 90% | 92% | 89% |
| 80 Plus Titanium | 90% | 92% | 94% | 90% |
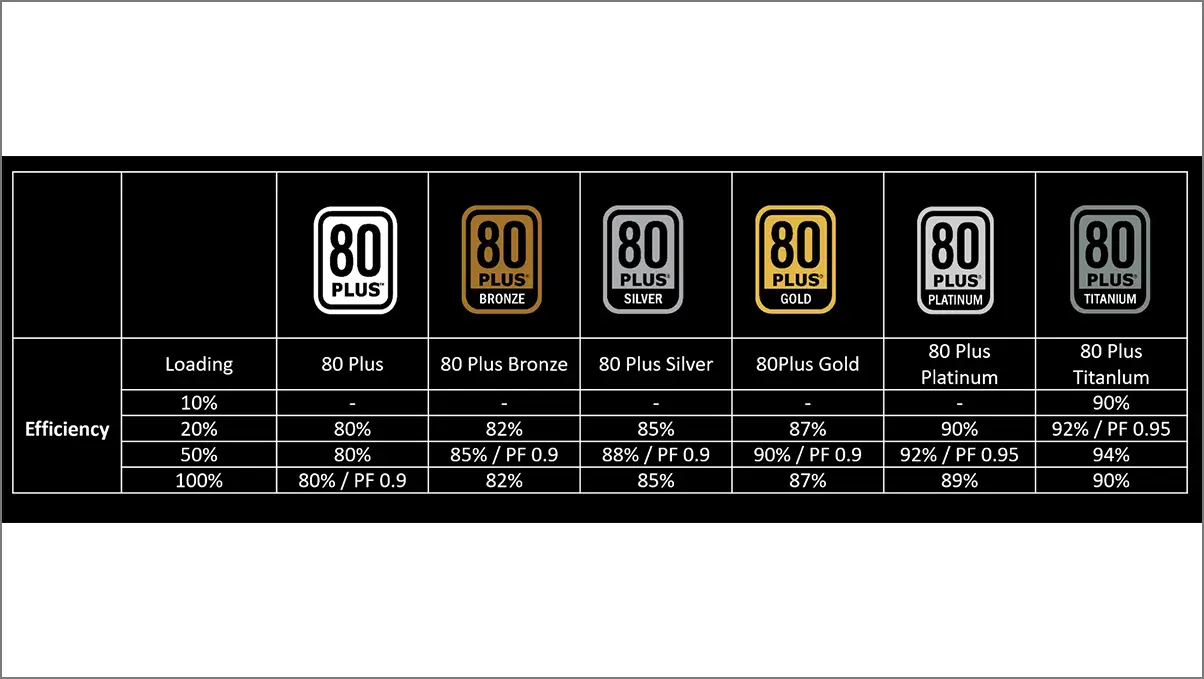
In general, people go with the 80 Plus Bronze and 80 Plus Gold PSUs depending on the wattage and pricing. For high-end PC setups or workstations, you can go with ATX 3.0 80 Plus Platinum or 80 Plus Titanium PSUs for higher efficiency.
4. PSU Connectors
When you buy a PSU from any manufacturer, it should come with all the required cables for connectivity. But you should be aware of which PSU connectors are for what, and sometimes, similar-looking cables may have different specifications.
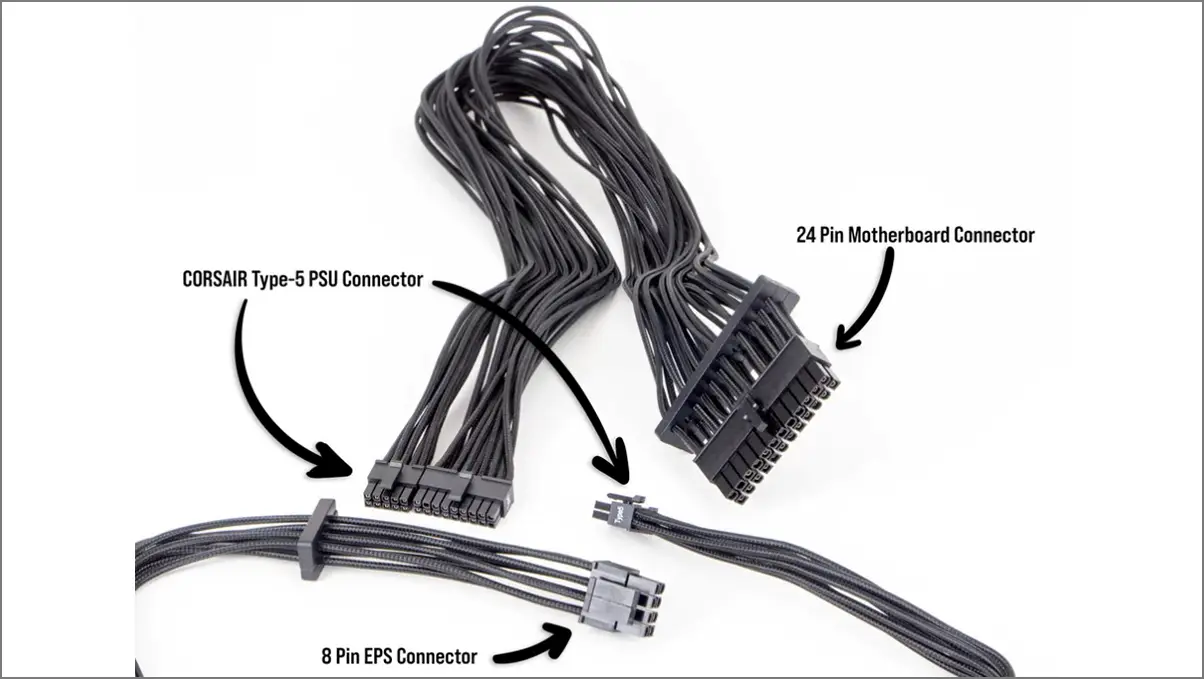
- 20+4 Pin ATX Motherboard Power Connector: It’s known as a main power connector that directly connects to the ATX motherboard to allocate power frequently.
- 4+4 Pin ATX 12V CPU Power Connector: It’s known as a CPU power connector (P4 power connector) and connects to a motherboard using ATX 12V power connectors.
- 6/8 Pin PCIe Connector: As the name suggests, it’s a PCI Express connector for components like graphics cards using 6, 8, 6+6, 8+6, 8+8, and some PSUs also provide 8+8+8 pin connectors. Check with your power supply connections before buying a GPU.
- 4-Pin Molex Connector: Molex connectors are considered peripheral connectors for hard disks or DVDs. It has become quite obsolete with modern technologies, but Molex to SATA power adapters and Molex to 3-pin fan adapters are still alive in the market.
- SATA Power Connector: The serial-ATA (SATA) power connector usually connects to SATA storage devices such as SATA hard drives, SATA SSDs, and SATA optical drives. It’s also used for fan controllers and RGB hubs.
5. Power Supply Cabling
There are three types of PSU cabling you can find below, depending on your budget and requirements:
- Non-Modular: These PSU cables come in a bunch and are attached permanently, resulting in more clutter and extra space required to adjust into the case.
- Semi-Modular: Only essential cables come in the fixed mode with semi-modular PSUs like motherboard and CPU cables. Meanwhile, the rest of the cables, like SATA, PCIe, and Molex, are removable.
- Fully Modular: You’re free to connect specific cables that you need to use with your PSU, as it’s designed for flexibility and convenience. It makes your PC build clean, has better airflow, and requires less space for cable management.
If your budget allows, you should always go with a modular PSU option for fewer cables. However, you can also choose a semi-modular power supply unit for your mid-budget PC build that will provide better performance and value for money.
6. Fan Spinning Noise
Try to get a power supply that doesn’t make a rattling noise when a fan is spinning under a considerable load. Of course, the power efficiency rating will come in handy for this scenario because a higher efficient PSU won’t take too much load and offers a silent operation throughout the years.
Some specific brands are also reliable for quiet PSUs, even at high fan speed. However, if your budget is tight, you can consider buying an entry-level PSU compromising with some noise.
7. Your Budget
The PSU is quite affordable as compared to other PC components like CPU, GPU, RAM, Motherboard, etc. But how do you decide the budget factor? Some popular PSU brands like Corsair, Cooler Master, Be Quiet!, EVGA, SeaSonic, Thermaltake, Gigabyte, Asus, MSI, etc, offer excellent power supply units in their category. However, a few brands provide premium PSUs.
Instead of focusing on the brand value, you should focus on the budget, specs, and additional features while picking a PSU. Check the PSU pricing category as follows:
- Entry-Level Build: You can go with a 400W-600W PSU at around the $40 to $70 price range, depending on the brand value, product quality, and 80 Plus Bronze/White certification. Suitable for basic computing like home/office or study purposes and basic gaming.
- Mid-Range Build: For mid-ranger PC builds like working or gaming with a dedicated GPU, you can choose a 600W-750W PSU in the $70 to $130 price range. It’ll offer 80 Plus Bronze/Gold certification.
- High-End Build: Hardcore gamers, multiple GPU users, or overclocking enthusiasts can go with a 750W-1,000W PSU in the $130 to $200 price category. It’ll offer 80 Plus Gold/Platinum/Titanium certification.
- High-End Workstations or Servers: For a $200+ price range, high-end workstations or server users can get a 1,000W+ PSU with 80 Plus Platinum/Titanium certification that can provide substantial power output.
Choosing the Right PSU for Your PC
In conclusion, selecting the suitable power supply unit for your PC build is crucial if you want optimal performance and long-term reliability. Try considering all the factors mentioned above before buying a PSU instead of mindlessly going with a higher wattage or brand name. You should also check for user forums and reviews of your chosen PSU model to get a better idea. A well-researched and highly compatible PSU is a kind of investment for your PC.