The display is the most important part of a laptop. So, when people start browsing for a new one; screen size and resolution are usually the first aspects people check off their list. But what if the underlying display technology could be the game-changer for your user experience? This guide will put into perspective, the main differences between the three most common types of laptop display panels: IPS, TN, and VA and discuss which one to go for when choosing your next laptop.
What is a TN Panel?

Let’s start off with the TN displays. Twisted Nematic (TN) Screen Technology is one of the earliest and most common types of liquid crystal displays. These panels were developed in 1970s. They offered a thinner and more energy-efficient to the then-dominant CRT monitors.
In a TN panel, the liquid crystals are sandwiched between two glass substrates and align themselves parallelly. When an electric current is applied, the crystals twist, allowing light to pass through and create the image on your screen.
Advantages of TN Panels
The biggest advantage of TN panels is their exceptionally fast response time. They can react to changes in 1 millisecond, making them very suitable for fast-paced activities, particularly for gaming purposes where every millisecond counts.
On top of that, manufacturing TN panels costs way less which contributes to their affordability, making them ideal among cost-sensitive consumers. This cost-effectiveness, combined with their speed, makes TN panels a popular choice for gamers and those who don’t need the highest color accuracy or viewing angles.
Disadvantages of TN Panels
Despite their speed, TN panels have several serious shortcomings. Their color reproduction is weak: for example, most TN panels can only reproduce the sRGB color space, and their contrast is relatively low. Typically, it ranges from 600:1 to 1000:1, although some models may reach slightly higher contrast ratios.
That makes TN panels not ideal for applications that require excellent color accuracy, for instance, when processing photos or videos. Additionally, their viewing angles are restricted to 170° horizontal and 160° vertical. So, the image will distort when viewed from a wider angle.
What is an IPS Panel?

IPS is a pretty popular option when it comes to laptop displays. It stands for In-plane switching (IPS) and was developed in the mid-1990s by Hitachi to address the limitations of TN panels, particularly in terms of color accuracy and viewing angles.
When using an IPS panel, liquid crystal molecules align parallel to the glass substrates. However, unlike TN panels, where the molecules twist, the molecules in IPS panels rotate within the plane of the display, which allows for better light transmission and color consistency.
Advantages of IPS Panels
IPS panels exhibit excellent color accuracy and uniformity. They can cover up to 100% of the DCI-P3 color gamut, making them perfect for graphic design, photography, and video editing.
They have extremely wide-viewing angles of up to 178 degrees both horizontally and vertically. So you won’t experience a brighter or duller picture. Because of these factors, IPS panels have become ideal for multitouch applications or situations where the screen is viewed by multiple people simultaneously.
Disadvantages of IPS Panels
While IPS panels excel in color and viewing angles, they lag in response time. Traditional IPS panels had a response time of around 4ms, but modern IPS panels have significantly improved, with some high-end models achieving response times as low as 1ms or even 0.5ms.
Additionally, they may suffer from backlight bleeding, where light can be seen around the edges of the screen, potentially affecting the quality of dark images.
What is a VA Panel?
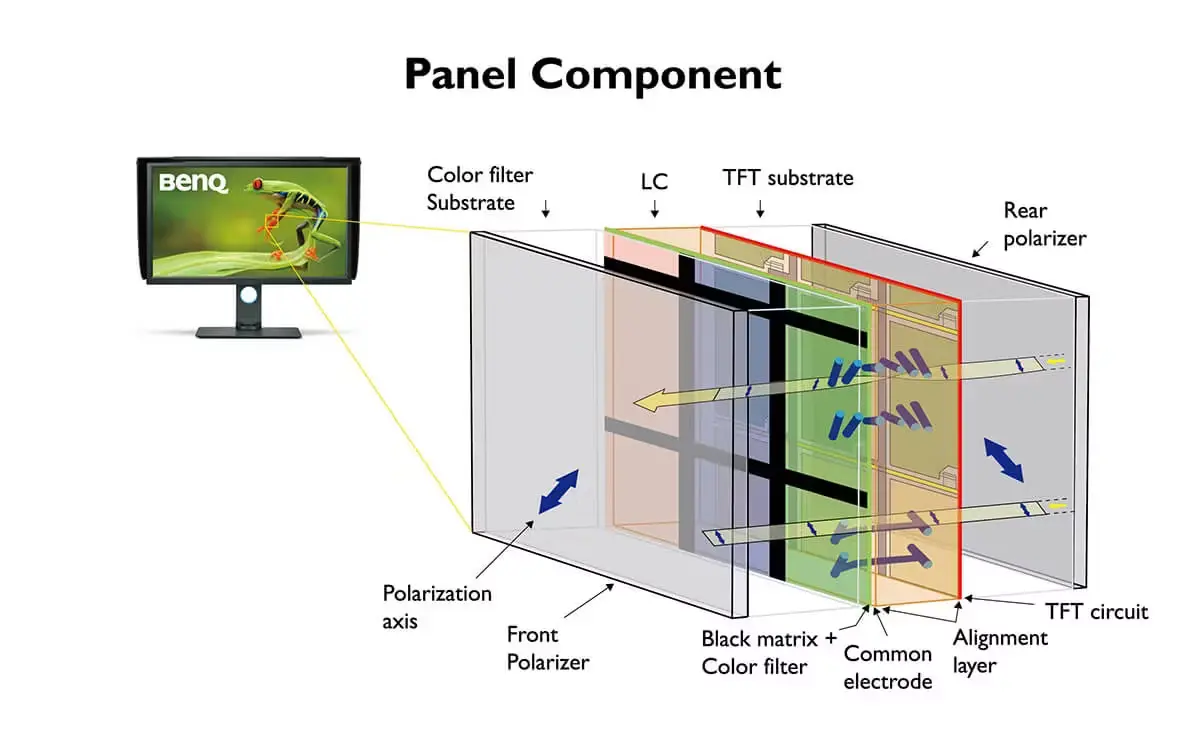
A VA panel is a good compromise between TN and IPS panels, originally designed by Fujitsu. The liquid crystal molecules in these panels are aligned vertically and at right angles relative to the glass substrates. When voltage is applied, the molecules tilt to allow light to pass through, thus achieving a balance between color accuracy, contrast, and response.
Advantages of VA Panels
VA panels boast high contrast ratios—usually within the range of 2500:1 to 6000:1. This makes black levels just instantly deeper and colors vibrant, in a way that makes VA panels great for media, video playback, and gaming.
While color reproduction is better than TN panels, it does not match the level of IPS. In addition, VA panels provide decent viewing angles, even though they are slightly less impressive than IPS.
Limitations of VA Panels
VA panels have been renowned for having slower response times, typically ranging from 4 to 5ms on average. Some motion blur and ghosting may be observed under certain conditions, making VA panels not optimal for competitive gaming.
Some newer models may reach lower response times, though they might still exhibit some ghosting compared to TN or fast IPS panels. Besides, their viewing angles are better than TN panels but not as spectacular as those based on IPS technology, which means some color shift should be expected from extreme angles.
IPS vs. TN vs. VA Panels: Table of Differences
| Features | IPS | TN | VA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color Accuracy | Excellent, covers up to 100% DCI-P3 | Basic, covers only sRGB | Good, better than TN but not IPS-level |
| Viewing Angles | Wide (178° horizontal/vertical) | Limited (170° horizontal/160° vertical) | Decent, but slightly less than IPS |
| Response Time | Good (Typically 1-4s) | Fastest (1ms) | Slowest (4-5ms) |
| Contrast Ratio | Moderate | Low | High (2500:1 to 6000:1) |
| Best For | Professional work (design, editing) | Gaming on a budget | Media consumption, balanced use |
| Cost | Higher | Most affordable | Mid-range |
IPS vs TN vs VA: Which is Better and Why?
If speed and cost are your key considerations, TN panels are the fastest and most cost-effective option. However, if color accuracy and viewing angles are more important to you, particularly for professional tasks like graphic design, IPS panels are the superior option. And for individuals who prefer fast response times, the VA panel provides an excellent balance of contrast and color accuracy.
In terms of speed, TN boasts the fastest response times and is widely regarded as an excellent option for competitive gaming. IPS panels tend to have a slower response time than TN panels. However, IPS compensates for this by providing superior color fidelity and wider viewing angles. VA, on the other hand, offers the best contrast ratios, but the slowest response time.
IPS also possess the broadest viewing angles, which makes them perfect for collaborative settings. The viewing angles of the VA panels are much better than the TN, yet they are still subject to some form of color shifting at extreme angles. TN panels have the poorest viewing angles, which can be a deal-breaker if you look at your screen from the side frequently.
Wrapping It All
Choosing the right panel among the available types—IPS vs. TN vs. VA is a tough decision in every laptop buyers journey. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses. TN panels are great for budget gamers but with a need for speed; IPS panels are excellent for professionals needing the best color accuracy possible; and VA panels offer a middle ground for good contrast and decent response times. By understanding your priorities and how you plan to use the laptop, you can select the most suitable panel technology.


