RAM configurations for a desktop PC or a laptop can confuse many people while upgrading or building a new setup. The difference between single-channel and dual-channel RAM can impact the overall performance drastically. It majorly determines how the system works with memory to perform functions faster enough. A comparison between Single Channel vs Dual Channel RAM can be overwhelming. So, we’ve mentioned all the aspects here so you can decide which one is better for your usage.
In general, dual-channel RAM configurations allow the CPU to access data transfers through two channels at the same time for better performance. The single-channel RAM setup only works with one channel at a time and eventually falls short of performance. Though people can’t see any significant differences in basic tasks, playing heavy games or video editing can showcase the actual impact.
How Does RAM Work?
The RAM (Random Access Memory) is the printed circuit board that needs to be installed on the motherboard’s RAM slot. RAM works as a real-time cache storage device that the CPU uses to run applications and tasks. However, due to its volatile nature, RAM can’t store any data for longer, and cache data will be cleared after rebooting the system.
RAM is controlled by the system known as a ‘Memory Controller’ where the RAM is connected to this controller, which is commonly known as a ‘Memory Bus.’ The memory bus (a bunch of wires) also comes in three categories – Control, Data, and Address. Here, the Control wires in the Memory Bus send the task commands to the memory modules, which the system performs respectively.
As the name suggests, Data wires in the Memory Bus contain the data that needs to be carried to the memory controller from the memory or vice versa. The Memory Controller also defines the memory speeds for the memory module.
For instance, if the Memory Controller is set to the factory default clock speed at a maximum of 2400MHz for the RAM on a motherboard, the installed RAM will also work with the same clock speed even if it supports higher speed like 3200MHz. That means your RAM is not utilizing its full potential. So, the Memory Controller is like an instructor for the RAM module to work.
What is a Single-Channel RAM?
Single-channel RAM is a computer memory configuration that uses only a single channel for the processor to access memory from the installed RAM. In short, the CPU can access data from only one memory module 64-bit wide bus (in DDR4) at a time, resulting in an overall performance slowdown as compared to the Dual-channel RAM. However, standard applications and tasks go well on a single-channel memory if you don’t require heavy multitasking or gaming.
Single-channel RAM also indicates that you’re always limited to being stuck with only one RAM stick on the motherboard. Hence, you won’t be able to double-up your RAM configuration parallelly by keeping both the existing and new RAM together. That may seem like a restriction if you want your system to be future-proof for the next few years.
Characteristics of Single-Channel Memory
- Data Transfer Speed: The data transfer speed of the single-channel memory is relatively slower in real-life performance than that of the dual-channel memory.
- Memory Capacity: As we’ve already mentioned above, the single-channel RAM falls short when it comes to limited capacity. You can use only one RAM at a time and less scope for expansion.
- Performance: It’s suitable for basic computing tasks and programs like web browsing, watching videos, using MS Office apps, everyday study purposes, computer learning for children, etc.
- Cost: For low-budget laptops or PC builds, you can use single-channel memory for a cheaper price tag. Low-powered CPUs don’t require higher processing. So, it’ll be an excellent option for entry-level systems.
What is Dual-Channel RAM?
Dual-channel memory is a technology that allows the CPU to read and write the required data from the two memory channels simultaneously. It boosts the overall system performance and memory bandwidth significantly. This dual-channel memory ensures a faster data transfer speed between the RAM and CPU, making it an excellent choice for most modern PC users.
Benefits of Dual-Channel Memory
Here, we’ve provided you with some significant benefits of having a dual-channel memory setup on your motherboard.
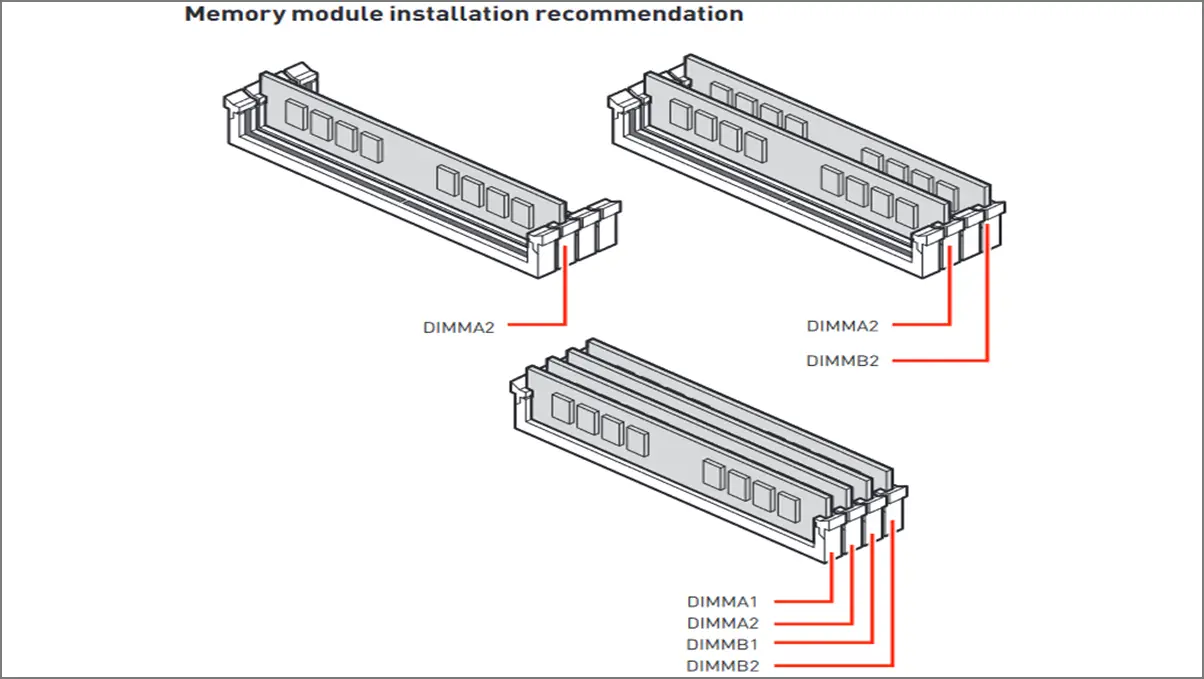
1. Memory Expansion
The memory controller uses both dual channels to connect with the processor in the dual-channel memory. It means you can use all four DIMM slots at the same time to expand your memory capacity. For example, you can use DIMM A1 and B1 together.
For additional RAM, you can also use DIMM A2 and B2 slots with A1 and B1 slots, but the same RAM variant should be installed. This also extends to two DIMM slot motherboards, where each slot is a direct channel for the CPU to utilize.

2. Boost in Bandwidth
Dual-channel RAM configuration offers a significant boost in memory bandwidth. It ensures a seamless, faster data transmission speed between the CPU and the RAM.
3. Better Multitasking
Dual-channel memory also allows a computer to handle multiple tasks at the same time without any performance slowdowns. It provides more effective memory management for running multiple resource-heavy applications like video editing, 3D rendering, games, photoshop, intense web browsing, etc.
4. Improved Gaming Performance
Almost every modern video game requires plenty of memory to run smoothly, along with other PC components like CPU, GPU, SSD, etc. Similarly, a dual-channel memory configuration on the system can also offer additional bandwidth to run PC games at higher frame rates.
5. Energy Efficiency
It’s also possible that using a dual-channel memory configuration can result in better energy efficiency and generate low heat, helping to achieve consistent performance in video games. Also, the battery backup can last for an extra few hours on laptops.
Keep in mind that your RAM kit, CPU, motherboard, graphics card, faster storage, CPU cooling, etc., should be compatible enough to unleash performance. Using the dual-channel RAM configuration alone won’t guarantee real-life performance unless the particular software and hardware combination is used.
6. Architecture Difference
Two identical RAM sticks mounted properly (usually in color-coded pairs of slots) will run in a dual-channel configuration, which allows for double memory throughput. Keep in mind that the number of channels is a CPU and motherboard limitation, so adding additional memory may or may not give you more channels depending on what platform you’re using.
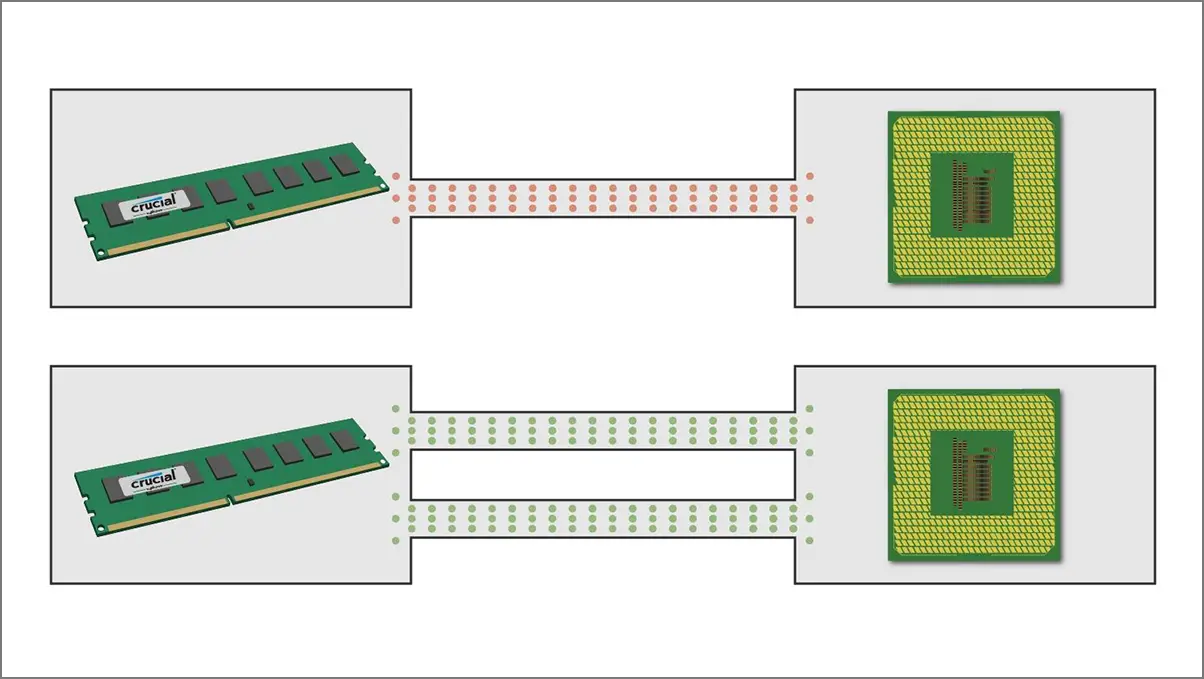
- Single-Channel RAM Architecture: To be precise, if you’re using a single RAM stick on a single-channel (single 64-bit data), it’ll only provide the data from a single lane.
- Dual-Channel RAM Architecture: In this scenario, the system uses two independent 64-bit wide buses (2x 64-bit data) at the same time to provide data. As a result, you’ll get doubled data lanes on the memory bus, which means a 128-bit (2×64-bit) channel is available to the memory.
7. Bandwidth
- Double-channel Memory: RAM bandwidth is the data transfer rate that a CPU can read/write into a semiconductor memory. It’s usually measured in megabytes per second (MB/s) or gigabytes per second (GB/s). Modern computing technology like DDR (Double Data Rate) can transfer two data bits per clock cycle, which means there are 128 bits of data in each cycle. The higher the number of DDR memories, the faster the bandwidth and the wider the bus. It should also match with the motherboard specs.
- Single-channel Memory: Whereas a single-channel memory bandwidth depends on the data bus width. That means a single channel only transfers 64-bit data in each clock cycle.
8. Interleaved Memory
Interleaved Memory is specially designed to manage the slow speed of DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) or uses a technique to divide the core memory into several modules. Usually, every memory module can have two or more memory banks for accessing data. This process delivers higher RAM throughput by using each memory bank to reduce the waiting time for data reading and writing.
As a result, the dual-channel memory outperforms in almost every aspect, mainly in heavy multitasking functions. You’ll get both increased memory bandwidth and reduced latency for large-scale systems, mostly with memory interleaving.
Single vs. Dual Channel RAM: Benchmarking Factors
Though benchmarking results may not always translate to real-life performance ratios, these tests can give you a better idea of how single-channel vs. dual-channel RAM delivers practically. We’ve gone through several benchmarking tests done by other PC enthusiasts, and it seems that dual-channel memory is categorically better than single-channel memory.
For example, a dual-channel Corsair Vengeance 8GB (2x 4GB) DDR3 RAM is ahead in a test against a single-channel Corsair Vengeance 8GB DDR3 RAM.
Single vs. Dual Channel RAM: Real-Life Performance
However, it seems that normal PC users won’t find any significant difference in the overall performance whether they use a single-channel or dual-channel memory. Even from a gaming perspective, the performance difference is quite negligible if we compare single-channel vs dual-channel memory.
If you’re expecting top-notch performance from your configuration, it’s always better to go with the dual-channel RAM specs. Of course, your CPU, GPU, and Storage should be powerful enough to get the most out of your RAM. You’ll get a stable FPS count on major games with these basics.
While talking about productivity and video rendering, plenty of reports claim that there is no drastic difference found in daily usage. However, dual-channel memory works better to reduce latency in some specific workloads than single-channel memory. In short, you may get up to a 10% jump in the dual-channel RAM performance during video editing.
Single vs. Dual Channel RAM: Power Consumption
- Single-channel RAM: It typically consumes less power because it only uses one module at a time. RAM modules consume power depending on the operating voltage, such as 1.2V for DDR4 or 1.35V for high-end RAM. It consumes 2-5 watts under normal load and can go up to 10 watts in heavy workloads.
- Dual-channel RAM: It uses two RAM sticks at a time and usually consumes high power since both modules are active. You can expect the power consumption in dual-channel memory to be slightly higher with multiple RAM sticks. Though modern DDR4 and DDR5 RAM modules are highly power-efficient, they can consume around 2-10 watts depending on memory type and capacity.
Single vs. Dual Channel RAM: Compatibility
Depending on your usage and preference, you should check the motherboard documentation carefully to determine whether it has single-channel memory or dual-channel memory. You should also check whether the DDR generation matches the RAM stick you have.
Single vs. Dual Channel RAM: Price
- Single-channel RAM: Most budget-segment PCs or laptops come with single-channel DDR4 RAM between 8GB and 16GB, which is a cost-effective option. The price ranges from $20 to $80, depending on capacity and speed. While DDR5 RAM is more expensive, it’s a good choice to be future proof with new systems.
- Dual-channel RAM: A dual-channel DDR4 RAM kit (2x 8GB = 16GB) will cost around $45 to $100, offering best-in-class performance for hind-end gaming and heavy multitasking. Meanwhile, the DDR5 RAM kit can be pretty expensive, ranging from $70 to $110 for a 16GB kit (2x 8GB). Again, it’ll offer futureproofing with high performance.
What’s Better – Single Channel vs. Dual Channel RAM
If you’re planning to build a new PC or just want to upgrade your system, a higher RAM capacity is essential. Though a single-channel RAM setup is quite adequate for basic computing needs in your daily life, configuring a dual-channel memory setup will deliver much smoother system performance overall. You can notice an exceptional boost when it comes to actions such as heavy multitasking, content creation, and hardcore gaming. If your budget allows, make sure you get a motherboard with dual-channel RAM support and a pair of RAM sticks with the same specs.


