The motherboard is the backbone of your PC, ensuring seamless communication between components like the CPU, GPU, and RAM. While often overlooked, it’s crucial for unlocking your system’s potential. Choosing the right one involves more than just budget and processor compatibility: you must consider the CPU socket, form factor, memory support, ports, slots, and brand reputation. Let’s see everything you must look for to choose the perfect motherboard for your PC.
What Is a Motherboard and What Does It Do?
A motherboard is a printed circuit board (PCB) equipped with slots and ports to connect components like the processor, RAM, storage drives, cooling fans, graphics cards, and power supply. It ensures stable communication and smooth coordination between these parts.
While newer motherboards may feature upgraded aesthetics, connectivity, and components like expansion cards and memory modules, their core function remains the same—routing signals and power to run the system efficiently.
What Type of Motherboard Should You Choose?
Here are the key factors to consider when choosing a motherboard for your PC build. Let’s dive in!
1. Set a Budget
Set a budget for your motherboard, factoring in the cost of other components. High-end motherboards offer features like overclocking and PCIe 5.0 but are pricier, while mid-range boards handle gaming and heavy apps well without the premium features. Choose based on your needs and budget.
A low-budget PC build may lack performance, future-proofing, and essential features like expansion slots and ports. For a powerful gaming PC, invest in a motherboard that matches your build’s capabilities. A budget of $150 to $250 typically offers a well-rounded motherboard with great performance and features.
2. Decide Which Processor You Want
The CPU (Central Processing Unit), or processor, handles all tasks in a PC. Since the CPU socket on a motherboard only supports specific processors, you’ll need to decide on the CPU first.
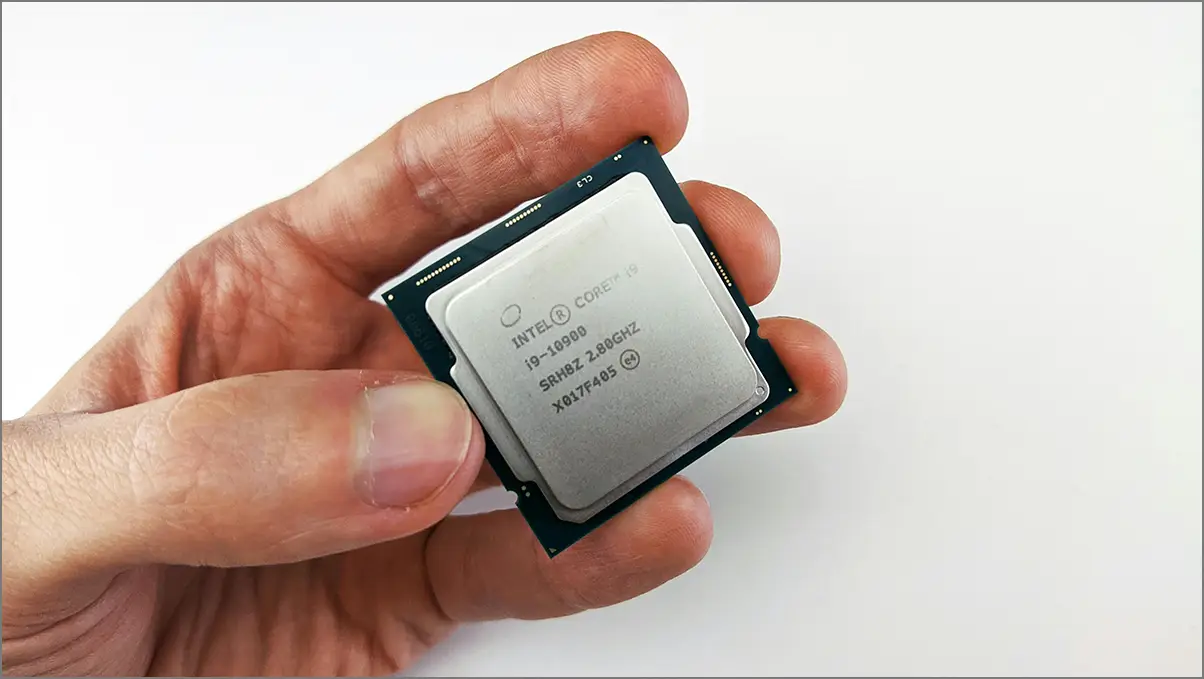

Your choice of CPU manufacturer—Intel or AMD—will determine the compatible motherboard, as CPUs and motherboards are not cross-compatible. Additionally, not all Intel CPUs work with every Intel motherboard, and the same applies to AMD. Ensure the CPU and motherboard are specifically compatible.
3. Choose a Compatible CPU Socket
The CPU socket is a slot on the motherboard that securely holds the processor and facilitates mechanical and electrical connections. Compatibility is key—a CPU must match its socket type. For example, an Intel Core i5-12400 requires an LGA 1700 socket, while a Ryzen 5 7600X works with an AM5 socket.

There are several common Intel and AMD CPU sockets widely used in the consumer market. Here’s a list of the most popular ones:
| CPU Socket | CPU Series / Generation |
|---|---|
| Intel LGA 1700 | 12th Gen Core |
| Intel LGA 1200 | 10th/11th Gen Core |
| Intel LGA 2066 | 10th Gen Core |
| Intel LGA 1151 | Intel 8th/9th Gen Core |
| AMD AM5 | Ryzen 7000 series |
| AMD AM4 | Ryzen 1000/2000/3000/5000 series |
| AMD sTRX4 | Ryzen Threadripper 3000 series |
| AMD TR4 | Ryzen Threadripper 1000/2000 series |
4. Pick a Compatible Chipset
Your CPU brand determines the compatible motherboard chipset, as each is designed for specific CPU generations. The chipset manages connections between the CPU, RAM, storage, and peripherals. Higher-end motherboards offer advanced chipsets with extra PCIe slots, USB ports, better configurations, and support for features like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and overclocking.
You can check the compatible chipsets with the CPU sockets and CPU generation below:
| CPU Socket | CPU Series / Generation | Compatible Chipsets |
|---|---|---|
| Intel LGA 1700 | 12th Gen Core | Z690, H670, B660, H610 |
| Intel LGA 1200 | 10th/11th Gen Core | Z490, H470, B460, H410 |
| Intel LGA 2066 | 10th Gen Core | X299 |
| Intel LGA 1151 | Intel 8th/9th Gen Core | Z390, Z370, Z370, Q370, H370, B365, B360, H310 |
| AMD AM5 | Ryzen 7000 series | X670, X670E, X870, X870E, B650, B650E, A620, PRO600 |
| AMD AM4 | Ryzen 1000/2000/3000/5000 series | X570, X470, X370, B550, B450, B350, B450, A320, X300, A300 |
| AMD sTRX4 | Ryzen Threadripper 3000 series | TRX40 |
| AMD TR4 | Ryzen Threadripper 1000/2000 series | X399 |
5. Motherboard Form Factor
There are mainly three types of form factor you’ll find in motherboards with different sizes. Now, you’ll have to choose which motherboard size you require depending on the budget, space, etc. If you want a full-size tower case, you’ll need enough space. The different motherboard sizes also determine the number of expansion slots, PCIe sizes, Dual In-Line Memory Modules, M.2 slots, and more.
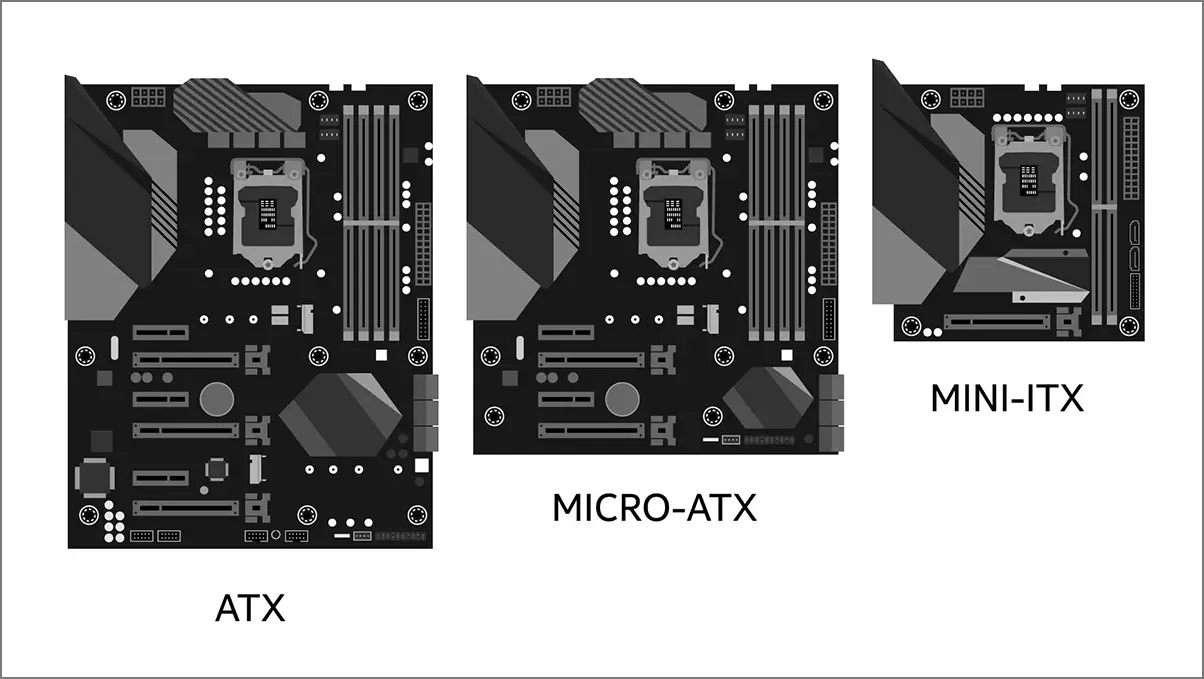
ATX motherboards (12″ x 9.6″) are the standard full-size option, offering easy builds with plenty of room. Micro ATX (9.6″ x 9.6″) is more compact, fitting mini-tower and full-tower cases, and includes two full-size PCIe slots and four DIMM slots.
Mini-ITX (6.7″ x 6.7″) is the smallest, designed for compact cases with limited cooling options but can support radiators in specific cases. It typically features one full-size PCIe slot and two DIMM slots but may lack additional ports and expansion options.
6. Expansion Slots and Ports
When choosing a motherboard, consider the expansion slots and ports needed to connect components like the CPU, GPU, storage devices, and networking cards. Key to this is PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots, available in x1, x4, x8, and x16 sizes.
The x16 slot is the most common for high-bandwidth devices. While PCIe 4.0 is the current standard, high-end motherboards now support PCIe 5.0 for even greater bandwidth.
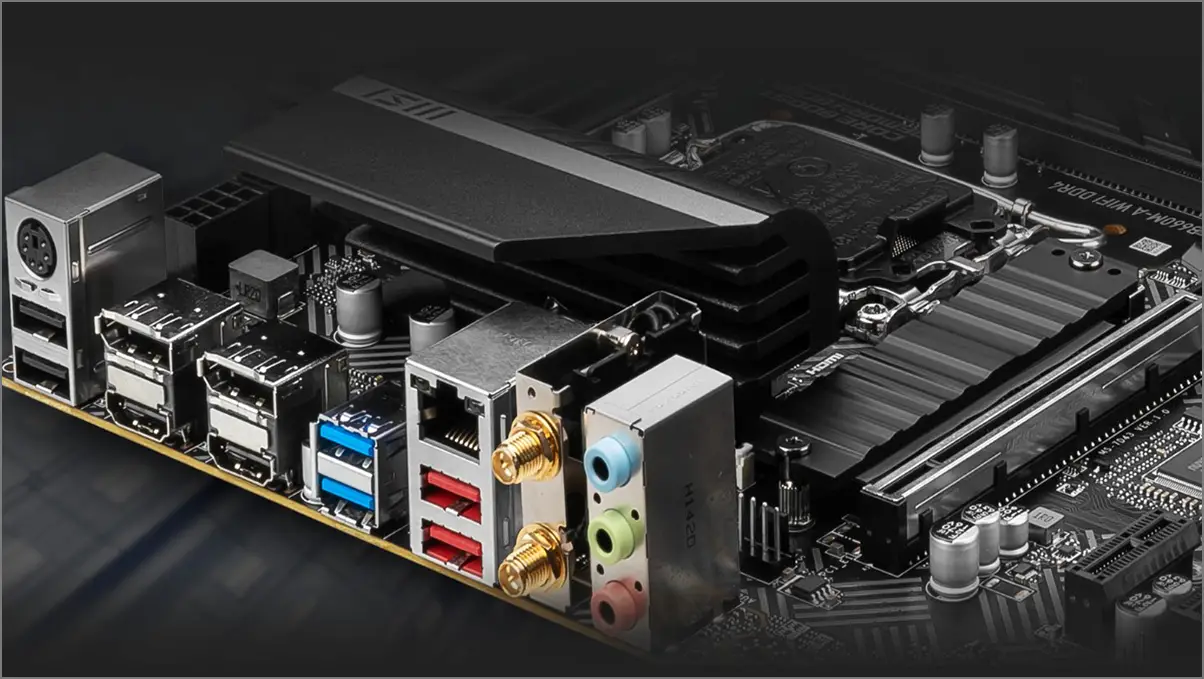

Considering the slots and ports, you should require at least USB 2.0 ports, USB 3.0 ports, 1x USB Type-C port, HDMI & DisplayPort, VGA port, Audio ports, an Ethernet port, a PS/2 port, SATA ports, Wi-Fi Card, Bluetooth adapter port, etc. For wireless connectivity, your motherboard should support Wi-Fi 5.0 or later and Bluetooth 5.0 or later.
7. RAM Capacity
Identify your RAM needs and ensure the motherboard has enough slots to accommodate them. For future-proofing, opt for dual-channel RAM slots. For intense gaming or heavy applications, a motherboard with four slots for a dual-channel setup is ideal.

It will ensure better performance, and you’ll have an option to upgrade RAM sticks in the future. Check for supported RAM capacities like 16GB, 32GB, or 128GB on the motherboard with supported RAM speeds (measured in MHz). Additionally, check the motherboard specs for overclocking your RAM.
8. Storage Options
When buying a perfect motherboard for your PC, check for the storage options. It’ll ensure compatibility with hard drives (HDDs), solid state drives (SSDs), and future storage expansions too.
First, you should check for SATA (Serial ATA) ports which are used to connect hard disks, 2.5-inch SATA SSDs, optical drives, etc in a standard way. The SATA port details can be found on the motherboard specs.
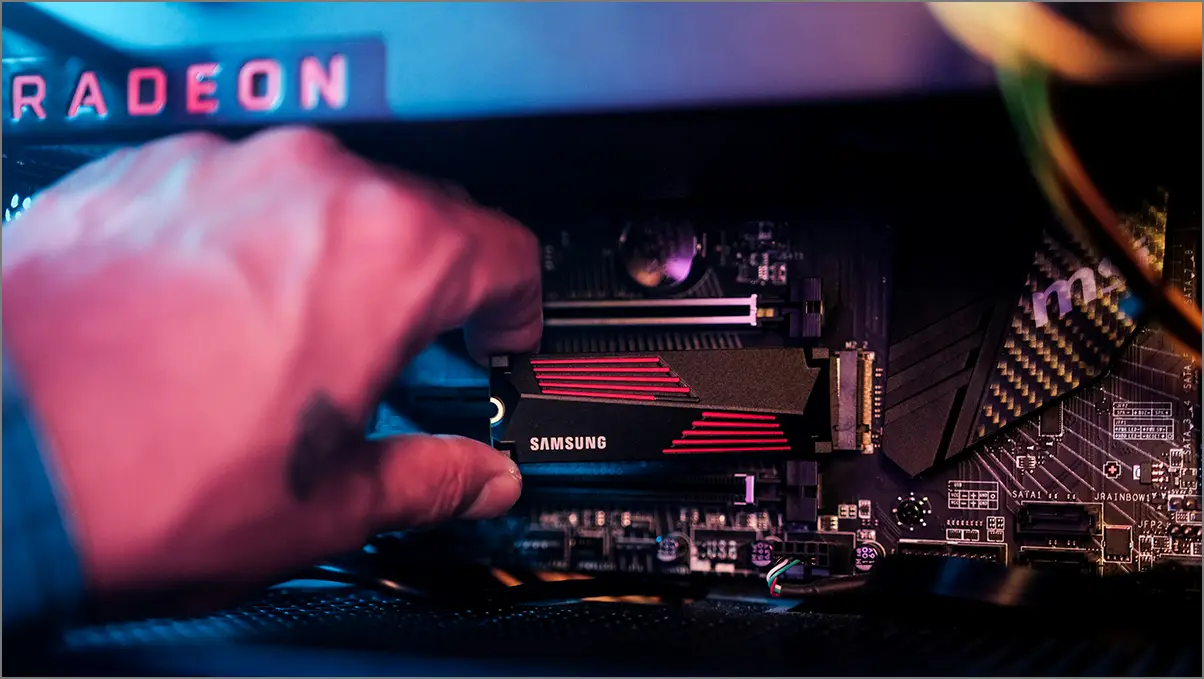

Next, look for M.2 slots on your motherboard to support faster, more compact M.2 SSDs. M.2 slots are compatible with both NVMe and SATA SSDs, but NVMe offers faster data transfer speeds. Check the motherboard specs for the number of M.2 slots and ensure they support PCIe NVMe or SATA M.2 storage.
9. GPU Compatibility
If you want to go with a dedicated graphics card for your PC build, make sure to check for GPU compatibility with your motherboard. Though some Intel CPUs and AMD APUs come with integrated HD graphics to provide display, they aren’t powerful enough to handle the heavy tasks of gaming and video editing. Therefore, an external graphics card is the ultimate solution.
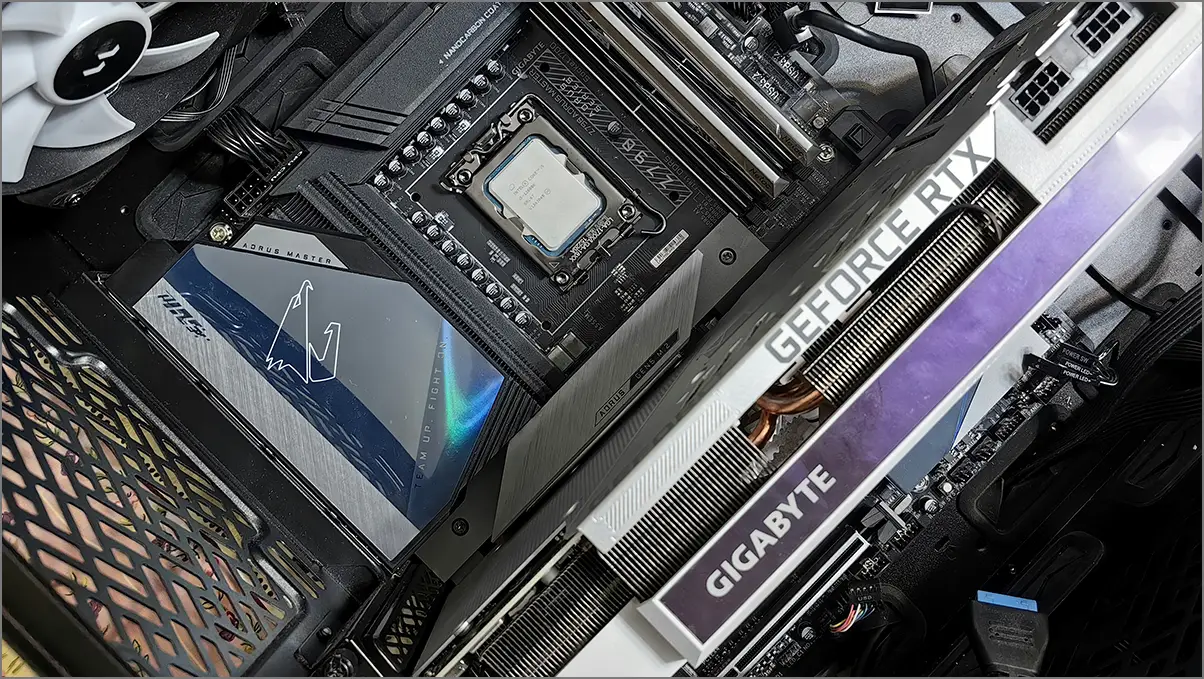

For the latest GPUs, ensure your motherboard has a PCIe x16 slot that supports Gen 4.0 or Gen 5.0 for optimal performance. Also, consider the graphics card’s physical size, form factor, and the required power supply wattage.
10. BIOS or UEFI Support
A well-optimized BIOS/UEFI support on the motherboard is another necessary aspect when choosing the right motherboard for your PC. It will allow you to use advanced features like memory overclocking, fan controls, hardware monitoring, tweaking advanced BIOS settings, and more. Most of the popular brands offer BIOS with future updates.
11. Overclocking Feature
Overclocking can be a personal choice and not meant for everyone. If you plan to overclock, ensure to check compatibility with your CPU and the motherboard like Intel Z-series chipset-compatible motherboards (e.g., Z790). For AMD CPUs, you can usually go with AMD B-series and X-series chipset motherboards.
12. Brand and Reliability
Popular brands like ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, and ASRock offer reliable motherboards across all price ranges. While the options may seem overwhelming, checking user reviews and support forums can help simplify the decision. Focus on compatibility and features rather than brand name, as mid-range motherboards often provide essential features and future-proofing at an affordable price.
Choosing the Right Motherboard for Your PC
Choosing the right motherboard for your PC build doesn’t have to be stressful. It’s all about selecting a compatible combination of essential components. By comparing different brands and models using the methods outlined above, you’ll be able to find a motherboard that meets all your needs and ensures optimal performance for years to come.