RAM is a necessary computer component for desktop PCs or laptops. But most people don’t think much about RAM when building a PC. We usually do not pay attention to factors like RAM size, generation, compatibility, and speed.
However, without having compatible RAM, you might not get optimal performance from your PC. So, if you’re looking for RAM without any proper idea, you can check this guide on how to pick the best RAM for your PC.
What is RAM?
RAM stands for ‘Random Access Memory’. It’s a type of computer memory that temporarily stores essential data, allowing the processor to run programs or open files much faster. RAM is volatile, meaning it is faster than SSDs in terms of performance. However, it does not function as a storage device, so temporarily stored data is wiped out when the power is turned off.
RAM is a printed circuit board that stores active data after an application is launched. It enables the CPU to operate faster by accessing the data. High-end RAM models often have higher data speeds, metallic heat spreaders, and heat sinks for improved cooling. Some RAMs even include RGB LED lights for aesthetic purposes.
Why is RAM Necessary for Your PC?
RAM is crucial for memory management and seamless multitasking on a PC. Without having compatible RAM and sufficient memory size, your system may not run smoothly. In most cases, you may encounter app crashes and slow response times.
Another critical point to consider is that RAM is responsible for smoother memory management in a system. If your PC does not have sufficient RAM, switching to multiple programs may require a refresh. In addition, running tasks may not respond well if memory is low.
Choosing the Best RAM for Your PC
Whether you’re looking to upgrade the RAM on your PC or want to build a new setup, be sure to cross-check all of the aspects mentioned below before making any purchase. Skipping any factor may cause potential issues with the compatibility or performance of the computer.
1. Determine the RAM Capacity
As mentioned previously, you may have heard that ‘more RAM means higher performance.’ This is a common practice, and most people follow this policy when buying a RAM. The RAM size is measured in gigabytes (GB). With sufficient RAM, more apps can run simultaneously without lag.
- 8 GB RAM: Having 8 GB of RAM is sufficient for a desktop or laptop computer for most tasks. From PC gaming to running practical applications, standard web browsing can be performed with 8 GB RAM.
- 16 GB RAM: The latest generation desktops and laptops come with a 64-bit processor and operating system that can support 16 GB of RAM or higher. Using 16 GB of RAM can be a sweet spot for hardcore gamers and heavy multitaskers. With 16 GB (2x 8 GB) RAM, you can live stream, play games, and make video conferences. It’s also useful for video editing, multitasking, and running heavy applications like Adobe Premiere Pro, Photoshop, etc.
- 32 GB RAM or Higher: If you’re a working professional to do tasks like 3D modeling and rendering, machine learning, heavy video editing, high-quality video production, data programming, and more, it’s suggested to use at least 32 GB of RAM or more. Of course, your CPU, motherboard, and other PC components should be powerful.
Even if you’re using high-end PC specs, there is a limit to using RAM up to 256 GB as much as possible. You can check the CPU and motherboard specs carefully to understand how much RAM is required. Make sure to check the documentation for your specific laptop or motherboard model to know more.
2. How Fast is the RAM (Speed)?
The RAM speed is measured in mega transfers per second (MT/s), but it’s different from the clock speed. Higher speed denotes a quicker response time to read and write requests. As a result, the RAM speed translates to the overall performance. Except for a few, most users may get confused by the RAM speed differences in the specifications.
There are two significant factors behind a faster memory speed: frequency and timing.
RAM Frequency:
RAM frequency commonly refers to its speed. When buying RAM, you might notice that RAM products are listed as DDR4 3200 MHz or DDR5 4800 MHz. Here, 3200 MHz or 4800 MHz refers to the RAM frequency. RAM continuously performs read and write cycles, which indicates the data cycle rate per second. It’s suitable for all memory-demanding tasks like gaming, rendering, or multitasking to operate smoothly.
DDR4-3200 refers to a 3200 MHz frequency cycle that goes through 3.2 billion read/write cycles (approx) per second. Therefore, a higher frequency rate is always better with each memory generation. However, the motherboard and CPU must support these higher RAM frequencies for optimal performance. Of course, high-frequency RAM is costly compared to low-frequency RAM.
Latency (CAS Timings):
The CAS latency is commonly known as ‘Column Access Strobe latency.’ It refers to the delay between the RAM getting a command from the CPU and the point of execution. You can usually notice CAS latency mentioned by the company on the RAM box and specs.
It’s a series of numbers that may look like 18-22-22-42. It is measured in clock cycles. The lower CAS latency number means better response time and faster data access. Brands use the CAS latency term with ‘CL’ in short.
For example, there are two RAM sticks available. One RAM has a CAS latency of CL16, and another one has a CAS latency of CL18. Here, the CL16 is lower, indicating faster performance because it will take fewer cycles to process the task command. So, try to buy RAM with low latency for your computer.
However, these differences shouldn’t have a significant impact on the daily tasks of modern PCs.
3. What Generation is it – DDR3, DDR4, or DDR5?
DDR memory generations in the PC world means different versions of DDR (Double Data Rate). The latest DDR generation or version is the fastest and most efficient compared to its previous generations. With each new generation, you’ll get improved speed, higher bandwidth, and better energy efficiency for intensive tasks.
Currently, the DDR4 memory is the standard and widely adopted generation among most PC users. Meanwhile, you can also get the latest DDR5 generation in the market for the highest possible performance. Of course, the DDR5 generation costs more and requires compatibility with the motherboard & CPU to work. You cannot mix the DDR4 and DDR5 RAM on the same system.
Similarly, you cannot use DDR4 and DDR3 RAM combined in a PC. Always go with a single DDR generation for your system, even while upgrading in the future. However, you can use a different DDR memory generation on your computer by upgrading both the motherboard and CPU to compatible models. You can check the most used DDR generation below:
- DDR3-Gen: Speed and performance are much improved compared to DDR2 generation. However, it has become quite outdated and only works with older machines.
- DDR4-Gen: Current standard generation for PC memory. It’s widely used due to its overall stability and affordable price. DDR4 generation RAM ranges between 2133 MHz to 3600 MHz or higher.
- DDR5-Gen: It’s the latest generation right now in the consumer market. Significantly faster and more efficient than its predecessor. Designed for high-performance tasks like gaming, editing, designing, AI, etc. DDR5 generation RAM starts from 4800 MHz frequency or higher.
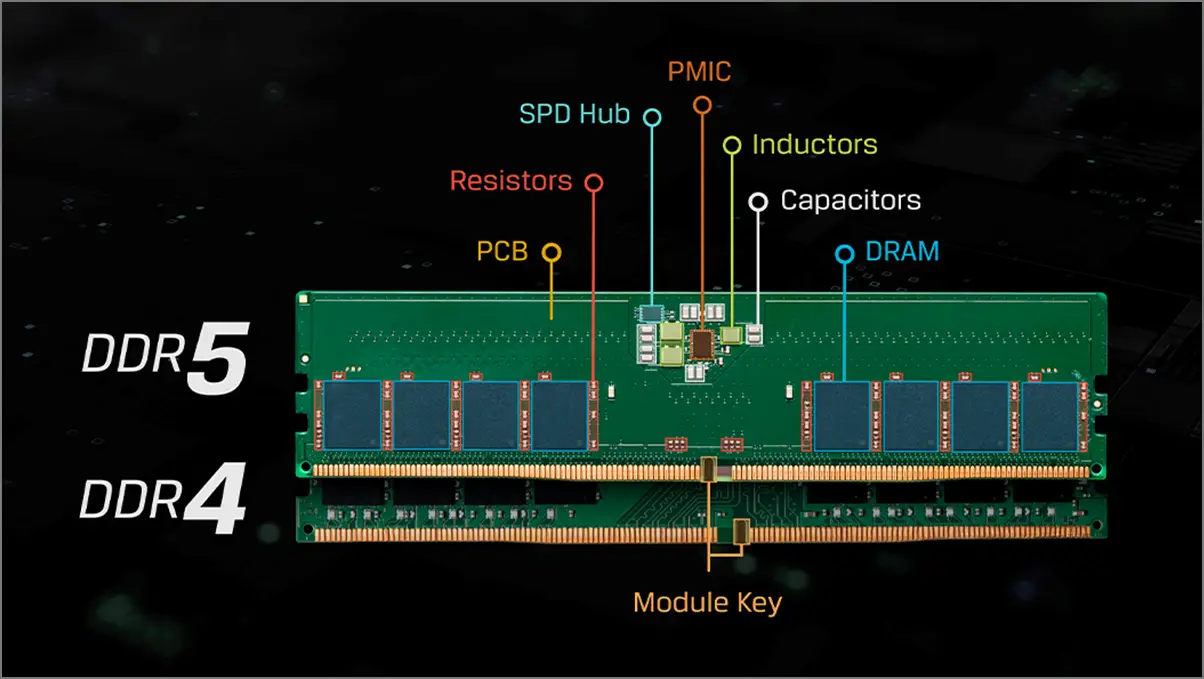
Please note that DDR4 won’t work on the DDR5 motherboard and vice versa. In short, you can use DDR4 RAM with a DDR4-supported motherboard and CPU. The same thing goes with the DDR5 generation. Most modern motherboards use DDR4 memory generation as a standard right now. For future-proofing and robust configuration, if you want to use the DDR5 RAM, you can pick the compatible motherboard and processor.
4. Also Check the RAM Form Factor
The PC RAM ‘form factor’ refers to the physical size and design of the RAM stick. It’s also useful to determine the overall compatibility with several computer types. It is necessary to check the form factor before buying a RAM stick so that it can easily fit into the memory slot of the computer. It applies to both desktop and laptop computers.
For example, the DIMM RAM is used in desktop computers due to its bigger physical size, and the SO-DIMM is used in laptops or compact devices due to its slightly smaller physical size.
You can check the different RAM form factors as follows:
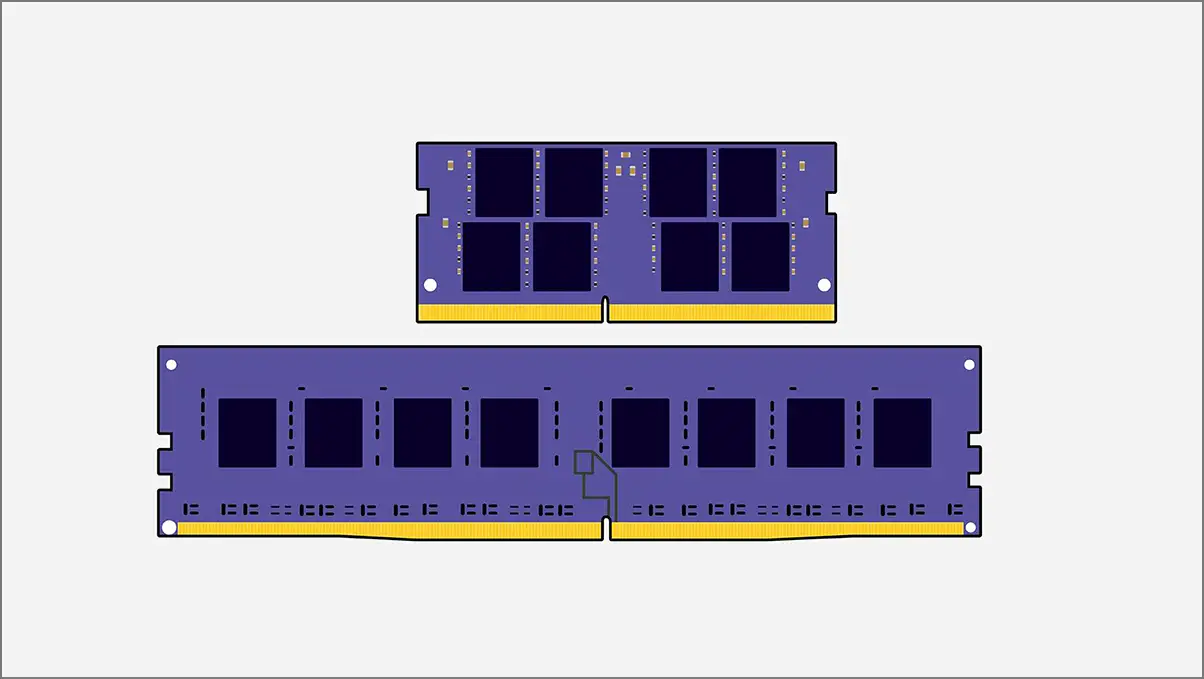
- UDIMM: It means unbuffered/unregistered DIMM, which is used on both desktop computers and workstations. This is the most common and standard RAM module type in the PC market. Offers high-speed performance and offers ‘x8’ or ‘x4’ memory chips.
- SO-DIMM: This can be used in laptops and compact devices like notebooks, mini PCs, etc. It’s also quite common and is also known as Small Outline DIMM (SO-DIMM).
- FB-DIMM: The fully buffered DIMM RAM is used in servers and complex workstations for more extensive processes and datasets.
- Registered DIMM (RDIMM): It’s used in servers and other applications for higher stability.
- Load-reduced DIMM (LR-DIMM): This RAM module uses isolation memory buffer (iMB) technology to minimize the load of the memory controller.
- MicroDIMM: The microDIMM (Micro Dual Inline Memory Module) is much smaller than the SO-DIMM RAM module. These RAM modules are used in ultrabooks, tablets, and small-sized laptops.
5. Single-Channel vs. Dual-Channel Memory
Single-channel or Dual-channel memory decides how the RAM can be installed on the slot and how it’ll be used to transfer data. Dual-channel memory allows a processor to access stored data from installed RAM sticks using two separate data paths simultaneously. It increases the data transfer speed and delivers high performance compared to single-channel memory (uses a single data path).
If you plan to build a new PC, use the dual-channel memory-supported motherboard. Of course, you’ll need to use identical RAM sticks in the correctly matched pair on the motherboard. It’s better to buy a RAM kit to utilize the dual-channel mode and memory overclocking fully. Meanwhile, you can go with a single-channel memory module for a low-budget desktop computer or laptop.
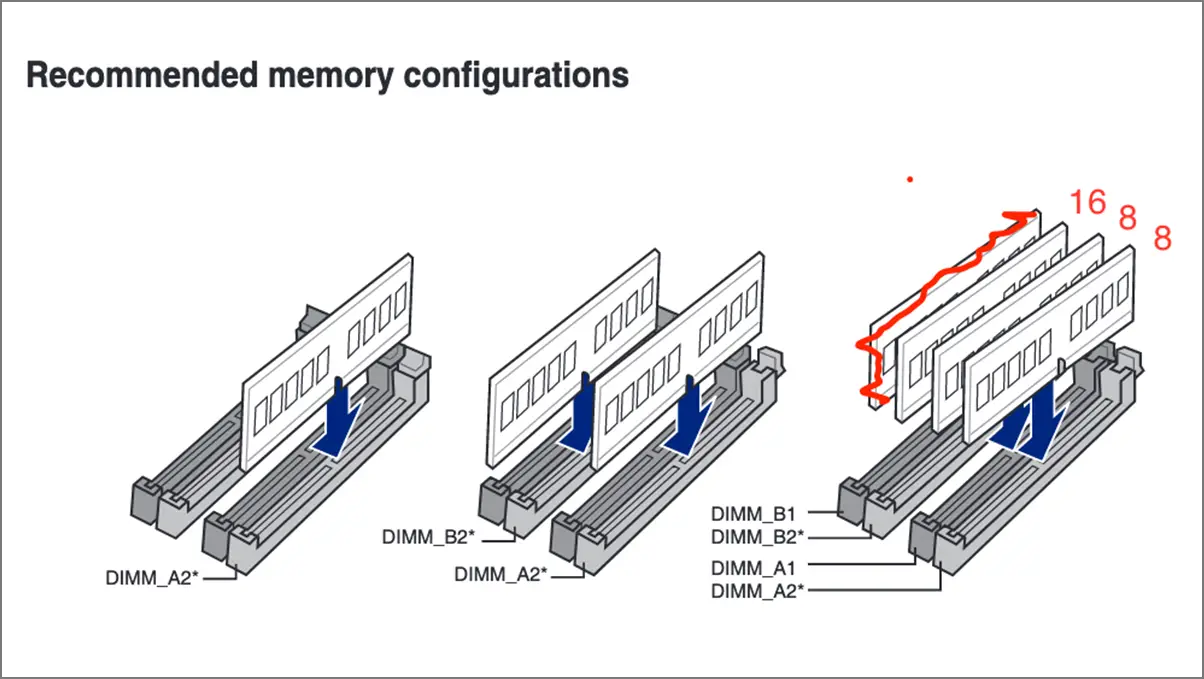
- Dual-Channel Memory: You can use two or more identical RAM sticks on a dual-channel memory module. For example, your motherboard has four RAM slots like DIMM A1, A2, B1, and B2, as you can see in the screenshot above. You can use two 4GB sticks instead of a single 8GB stick. Of course, the RAM capacity and speed should be the same.
- Single-Channel Memory: You can only use a single RAM stick on a single-channel memory module. It allows the computer processor to access the data only using a single path at a time. As a result, the overall data transfer speed and performance are compared to a dual-channel memory module. It’s easy to configure and cost-effective for basic computing tasks.
6. Heatsink and Heat Spreader
Some desktop PC users may find issues with enough space between the CPU heat sink. It mainly causes problems with the RAM installation. This may happen due to the limited space between the RAM slots and the CPU module area. Sometimes, a bigger air CPU cooler can also come close to RAM slots. So, always check for compatibility factors with the respective seller or online user reviews.
As RAM heat sinks and heat spreaders work to dissipate excessive heat, make sure to check if your RAM has effective heat spreaders and heat sinks before purchasing.
- Heat Spreader: It’s an attached component to specific RAM sticks that helps quickly transfer the excessive heat to a heat sink. A heat spreader is mainly made of copper or aluminum as a good heat conductor. This helps keep the RAM cool and maintains optimal performance.
- Heat Sink: It is a cooling component (passive heat exchanger) that quickly transfers heat from the RAM and dissipates it into the air. Heat sinks are mostly made of aluminum or copper. Heat sinks use fins to improve the airflow with their increased surface area.
8. Check the Voltage
The RAM voltage is the electrical power level that allows it to function. The appropriate voltage will ensure that the RAM functions properly. An inconsistent voltage can cause RAM overheating or damage. Of course, the RAM voltage can affect the overall performance, mostly with overclocking. Although a higher RAM voltage helps maintain stability while running at higher speeds, this often increases overheating.
The higher RAM voltage also causes higher power consumption overall by the system. Therefore, always check all voltage-related documentation of the selected RAM that can use a limited voltage.
9. A 32-bit PC May Not Support Your RAM
Most modern laptops and desktop PCs have a 64-bit operating system, which allows users to use higher RAM capacity. If you use a 32-bit Windows operating system on your computer, you can only use up to 4 GB of RAM. That’s the major limitation of a 32-bit Windows system.
10. ECC and Non-ECC RAM
- ECC RAM: Error Checking and Correction (ECC) is a feature in some memory chips that helps prevent data errors and corruption. It can also fix some issues automatically to avoid data loss. ECC RAM is generally used in workstations or servers to handle essential data like data analysis and machine learning. However, it offers slow performance due to multiple cross-checks. The best part is that most consumers do not require ECC RAM.
- Non-ECC RAM: It’s a common type of RAM mainly used overall on consumer PCs. Non-ECC RAM doesn’t have any error-checking or fixing capabilities. It can be slightly faster in performance than ECC RAM. Non-ECC RAM is ideal for everyday tasks like browsing, streaming, multitasking, gaming, and more.
11. Does it Have Overclocking Support?
Memory overclocking is the process of maximizing the speed (frequency) of a computer’s RAM (Random Access Memory). It helps achieve faster data transfer speeds than its default speed. With overclocking, users can perform memory-intensive tasks at higher speeds with improved performance.
You can also overclock your RAM to its maximum frequency using the BIOS. Most manufacturers provide RAM with a default speed (frequency). Fortunately, Intel-certified RAM kits support overclocking via Intel XMP (Extreme Memory Profile). In addition, AMD allows its users to overclock RAM using AMD EXPO.
12. Lastly, Does it Look Good?
You can also consider buying a basic or aesthetically pleasing RGB RAM stick to match your desk setup. There are three types of RAM sticks you can get on the market: basic, standard, and RGB shield designs. To get RGB effects for a gaming PC or desk setup, you can choose an RGB shield design. Otherwise, you can get a standard or basic design for a minimal appearance.
Picking the Best RAM for Your PC
Here’s how to choose the best RAM for your computer. Your choice depends on your budget and desired performance. For a powerful PC, you may need faster DDR5 RAM with lower latency for maximum performance. However, low-budget or mid-budget PC users can go with 8 GB or 16 GB of DDR4 memory to get better value for the price.
We suggest you go with dual-channel memory with a higher frequency (speed), like 3200 MHz or higher, for optimal performance. For memory-intensive tasks like content editing or 3D rendering, you might need a minimum of 32 GB RAM or higher.
Choose the RAM wisely to save some money and hassle in the long term. To avoid upgrades in the near future, choose the latest-generation, compatible RAM with higher capacity. This applies to other PC components as well.


