Intel processor naming scheme can be confusing and complicated to understand for several consumers. This naming convention has evolved over a decade. The brand uses different factors to set specific naming schemes for some of its older and all new-gen CPUs. It seems Intel is removing the ‘i’ prefix from its processors to use a new naming scheme.
We may not see the Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 branding with Intel desktop or laptop CPUs anymore, though they’ve been used in the past. The new naming convention includes several aspects like product brand, performance tier, generation, SKU (Stock Keeping Unit), and suffixes.
So, identifying and selecting the right Intel CPU for your specific need or budget can be crucial. If you’re also new to it, check out this guide to understand better.
What Does the Suffix Mean?
Before jumping into the new naming schemes for Intel processors, this info will help you choose the suitable CPU model for your requirement without any suffix confusion. Here’s what the suffixes mean:
| Segment | Suffix | Purpose | Processor Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desktop | K | High performance, unlocked (i.e. applicable for overclocking, gaming) | Intel Core i9 processor 14900K |
| F | No integrated graphics (requires an external GPU) | Intel Core i5-12400F | |
| S | Special edition (optimized performance) | Intel Core i7-4790S | |
| T | Power-optimized for desktop PCs | Intel Core i3-4160T | |
| X/XE | Extreme performance and unlocked for overclocking | Intel Core i9-10920X | |
| Mobile (Laptop and 2-in-1) | U | Highest performance in the LGA package | Intel Core 7 Processor 150U |
| H | Highest performance | Intel Core Ultra 9 Processor 185H | |
| G | Includes built-in graphics | Intel Pentium Processor G3250 | |
| G1, G4, and G7 | Graphics level (processors with newer integrated graphics technology) | Intel Core i5-1135G7 | |
| HX | Highest performance, all SKUs unlocked | Intel Core i9-13900HX | |
| HK | Highest performance, all SKUs unlocked | Intel Core i9-12900HK | |
| HQ | Highest performance in the LGA package | Intel Core i7-7700HQ | |
| P | Performance optimized for thin and light laptops | Intel Core i7-1370P | |
| Y | Extremely low-power efficient | Intel Core i5-10310Y | |
| Embedded | E | Embedded (efficient cores) | Intel Xeon E-2400 |
| UE | Power efficient | Intel Core i7-8665UE | |
| HE | High performance | Intel Core i7-9850HE | |
| UL | Power efficient, in the LGA package | Highest performance in LGA package | |
| HL | Highest performance in the LGA package | Intel Core i7-10710HL |
How Are Latest Intel Processors Named?
According to Intel, a new naming scheme has been introduced to simplify the identification process. It’ll also indicate the performance level of the Intel processors. We all know that a higher number in the processor lineup like ‘Core i9’ indicates higher-tier performance than entry-level lineups such as ‘Core i3’.
Currently, the major naming convention starts from the 14th-gen Meteor Lake CPUs with the rebranding of ‘Core Ultra.’ So, the Intel Core Ultra lineup processors now use 3, 5, 7, and 9 rather than the older i3, i5, i7, and i9 branding. Meanwhile, the top-tier models are now rebranded as Core Ultra, for example, ‘Core Ultra 9’.
Now, the ‘Performance Tier’ and ‘SKU’ sections also play a significant role in product identification. The ‘Ultra’ term hints at the premium segment of the specific processor. It includes higher performance, premium cost, AI integration, and advanced graphics functionalities. However, it’s quite surprising that a few older Intel Core series CPUs still use the ‘i’ prefix branding, e.g., Core i7-13700K (desktop processor).
The processor number, brand name, specs, and benchmarking are essential factors for someone to consider before buying. It’s also important to know that Intel uses the numbers ‘5’ and ‘7’ in both ‘Core Ultra’ and standard ‘Core’ series CPUs. So, the Intel Core 5 CPU will not perform similarly to the Intel Core Ultra 5 CPU in any way. There will be drastic changes in performance, power consumption, pricing, and more.
Here, we’ve provided the following Intel CPU naming schemes with their suffixes to help you identify which Intel processor is the best for you:
- Intel Core Ultra Processors
- Intel Core Processors (Series 1)
- Intel 14th-Gen Core Desktop Processors
- Intel Processors N-Series
- Intel Processor
- Intel Pentium Silver and Gold Processors
- Intel Celeron Processors
Intel Core Ultra Processors
Intel Core Ultra CPUs are the premium range of processors for delivering excellent performance in high-end productivity, content creation, game upscaling, etc. So, Core Ultra processors include neural processing units (NPUs), 3D performance hybrid architecture, and built-in Intel Arc GPU1 for enhanced graphics and AI (artificial intelligence) acceleration.
According to the company, the Intel Core Ultra-powered premium laptop users will enjoy new AI capabilities on selected ultra processors with less power consumption. The Intel Core Ultra processor family lists the Intel Core Ultra 9, Intel Core Ultra 7, and Intel Core Ultra 5 processors that will directly indicate the performance level. Core Ultra processors have an SKU (stock keeping unit) number of 1 and 2, representing the Series 1 and Series 2 CPUs.
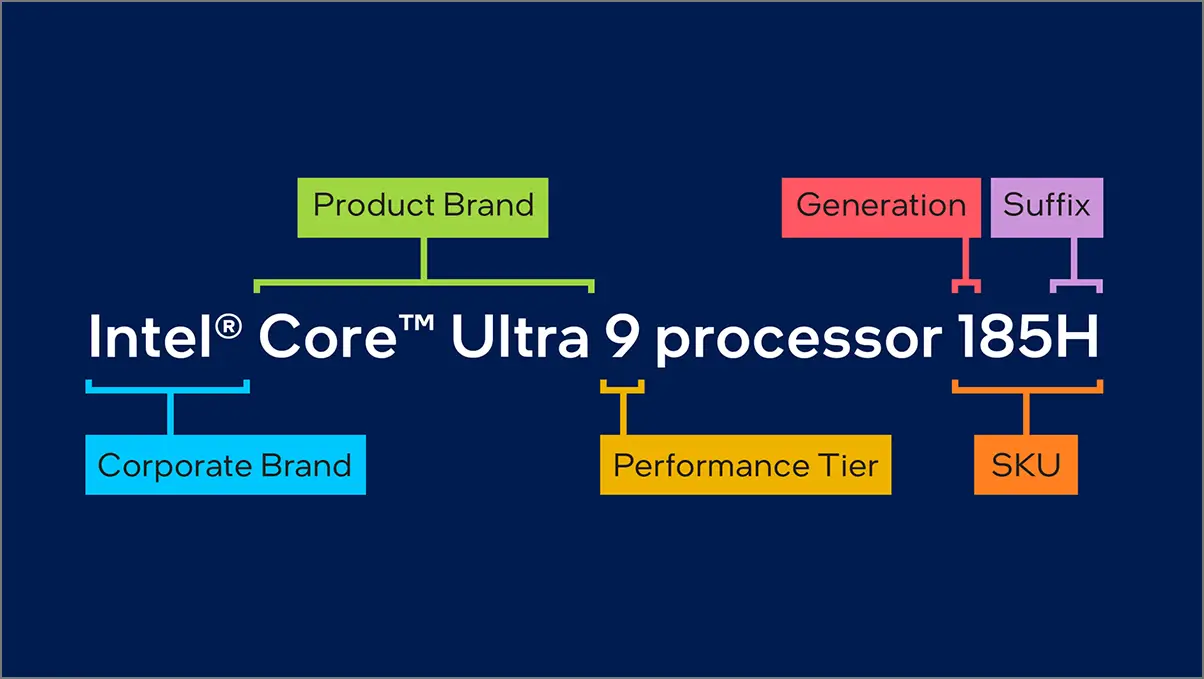
Additionally, you’ll get suffixes on Core Ultra processors like H, U, and V. For instance, Intel Core Ultra 7 processor 165H, Intel Core Ultra 7 processor 288V, and Intel Core Ultra 5 processor 135U. Here, the suffix ‘H’ indicates high performance, ‘V’ denotes virtual machine optimized, and ‘U’ denotes standard performance.
Intel Core Processors (Series 1)
Intel Core processors now include a new era of advanced naming schemes for the processor number in a 3-digit system. Intel Core 7 processor, Intel Core 5 processor, and Intel Core 3 processor family are one of them. So, the newly selected processors from the Core 7, Core 5, and Core 3 lineup won’t have i7/i5/i3 names anymore. It will be applied to standard laptops right now.
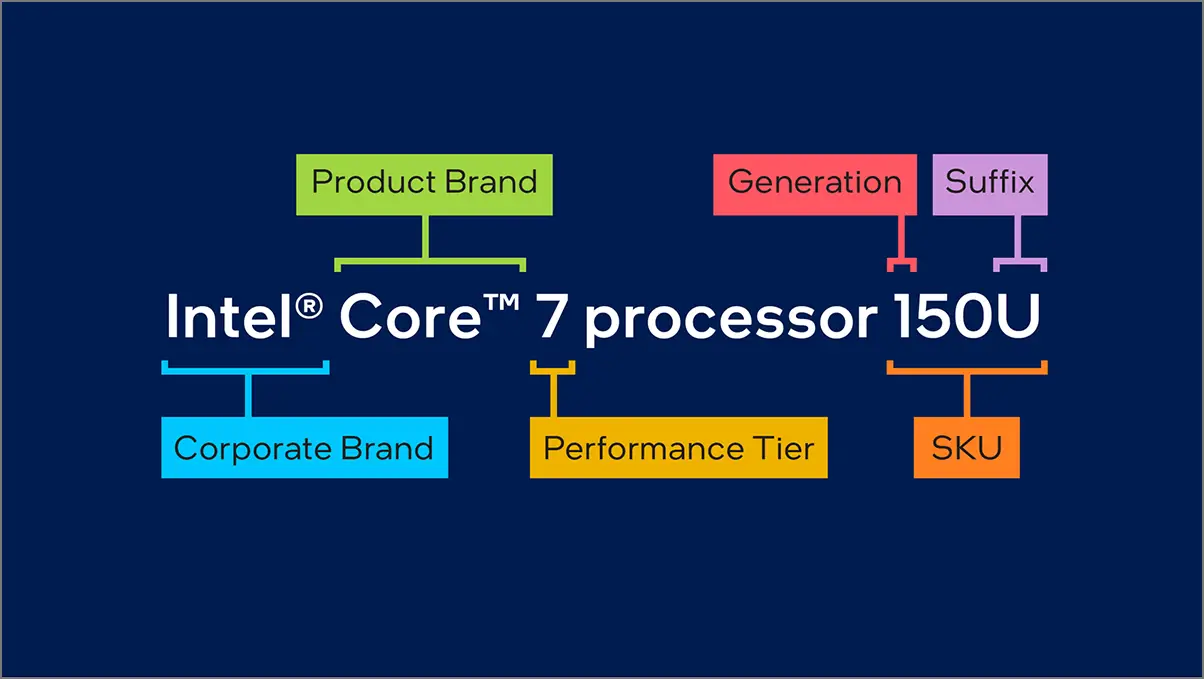
Intel mentions processor names like Intel Core 7 processor 150U, Intel Core 5 processor 120U, and Intel Core 3 processor 100U, respectively. Of course, the existing Core i9, i7, i5, and i3 processors will remain the same.
Intel Core Processors (14th-Gen)
Intel Core 14th-generation processors are designed to deliver high performance and high efficiency due to the new performance hybrid enhancement. The Core 14-Gen CPUs are also built on the Raptor Lake architecture for desktop models, similar to 13th-generation processors. This family includes Intel Core i9 processor, Intel Core i7 processor, Intel Core i5 processor, and Intel Core i3 processor, respectively.
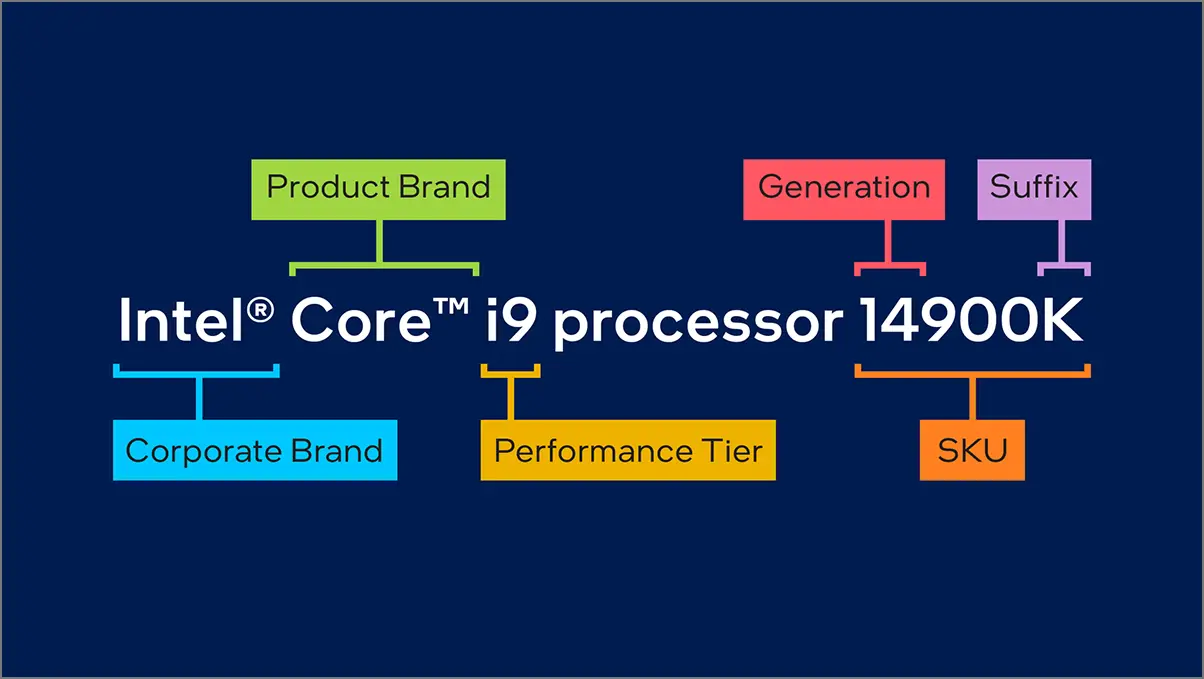
Intel has mentioned a Core 14th-Gen desktop processor like the Intel Core i9 processor 14900K where the ‘Intel Core’ is brand, ‘i9′ is brand modifier, ’14’ indicates generation, ‘900’ is SKU, and ‘K’ is suffix. Overall, the ‘14900K’ is the processor number. Again, it’s a little bit confusing as Intel keeps the same ‘i’ prefix for the naming scheme here. Remember that the lowercase ‘p’ for processor indicates nothing but a term only.
Intel Core Processors N-Series
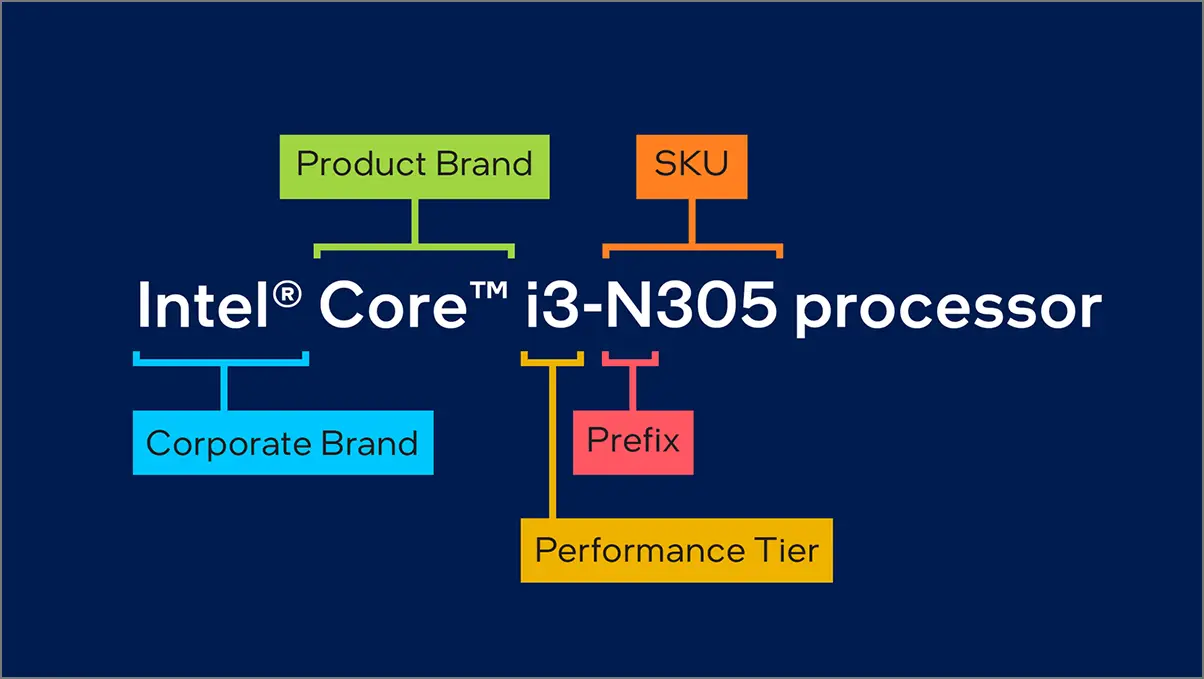
The Intel Core Processor N-Series offers a new lineup for entry-level computing CPUs on laptops and desktops. This N-series family is slightly improved than the Intel Pentium and Celeron lineup. The company has mentioned a processor like Intel Core i3-N305 processor as an example.
Intel Processor
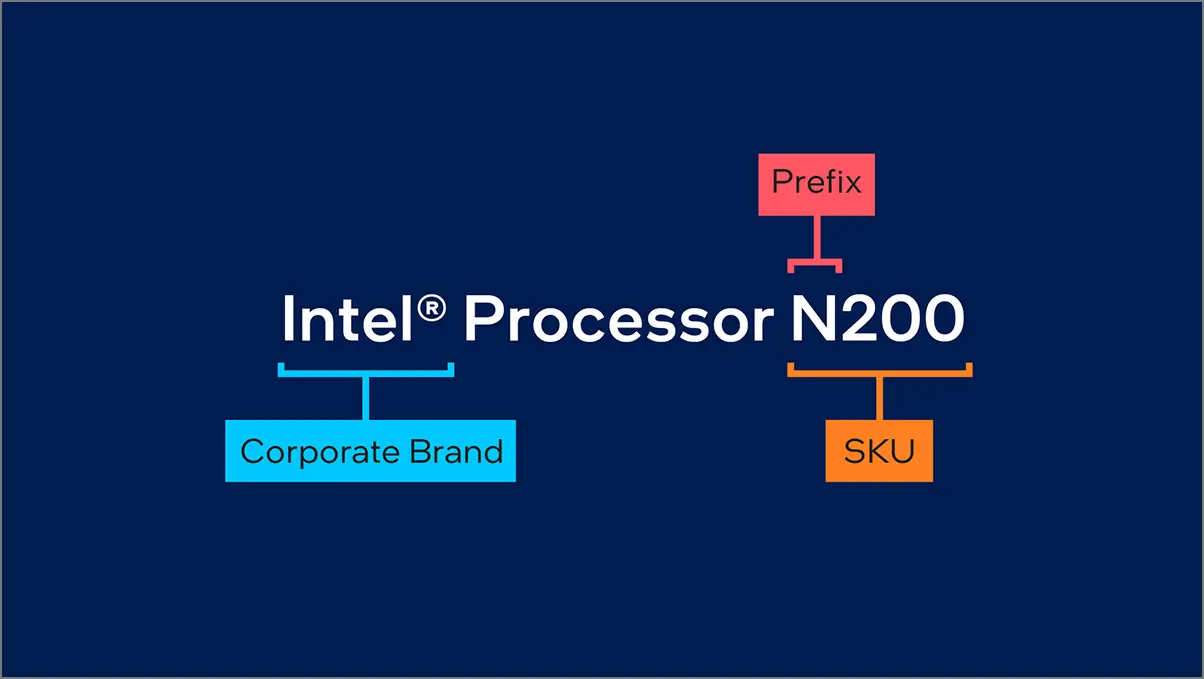
The all-new Intel Processor family offers ultra-low-powered chips for entry-level laptops and some desktops. This lineup builds on the same Intel Pentium and Intel Celeron brands with a few updated features. For this family, Intel does not provide a generation indicator. Only the prefix ‘N’ or ‘U’ will be there. Do keep in mind that uppercase ‘P’ in Processor now means a product brand for Intel’s N-series CPUs like Intel Processor N200.
Intel Pentium Silver and Gold Processors
Though new generation updates have been added to the Intel Pentium family processors, the company is striving to offer the same processors under the latest Intel Processor brand. It includes the existing Intel Pentium Silver and Intel Pentium Gold processors for low-end or entry-level computing experience. The Pentium Silver uses the same Atom & Celeron architectures, and Pentium Gold processors use the same Kaby Lake or Coffee Lake architecture.

In 2024, keeping the Pentium family won’t make any sense. Still, the company is most probably dealing with this lineup due to specific niche customers for affordable price segments like mini PCs, Chromebooks, low-end laptops, etc. Intel mentioned that the higher numbers inside the processor class will denote several improved features and benchmarks, including cache, clock speed, or front-side bus.

As per the company, Intel Pentium Gold and Silver processors have distinguished performance levels. For example, the Intel Pentium Gold CPUs are optimized for better performance, and the Pentium Silver CPUs are designed for an affordable price range with compromised performance. Intel has mentioned products like the Intel Pentium Silver N6000 processor and Intel Pentium Gold G7400 processor for reference. The higher number indicates better performance in this family.
Intel Celeron Processors
Last but not least, the Intel Celeron Processor references two different types out of some Celeron CPUs that may contain either a 4-digit number or a prefix/suffix respectively. For basic computing needs like education and online learning, you can go with Intel Celeron processors. The company has mentioned a few product names for reference, such as Intel Celeron Processor 7305L, Intel Celeron Processor 7305E, Intel Celeron Processor 7300, etc.

Here you’ll notice that Celeron processors do come with suffixes like ‘L’, ‘E’, or no suffix. As usual, the higher number means better overall performance, including cache, clock speed, etc.

Steps to Check Your Intel CPU Details
You can quickly identify the necessary details or at least the model number of your Intel CPU directly using your computer. Follow the steps below to find out:
Open the Start menu on your system and type msinfo. Now, click on System Information from the search result and click on System Summary from the left pane. Head over to the right sidebar to get all system-related details of your desktop or laptop.
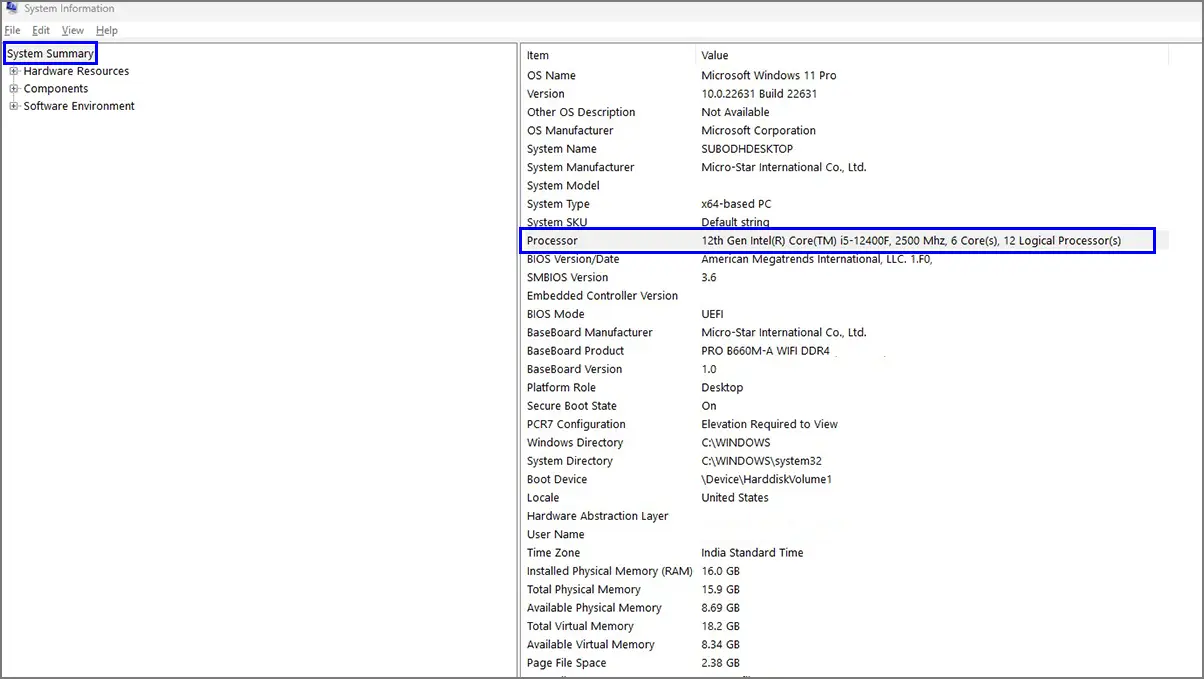
As we only require the processor details right now, check for the same. It’ll show you the processor model, generation, number of cores, and frequency.
Intel’s New Naming Scheme is Somewhat Confusing
It’s always necessary to identify the brand and model of the processor before buying to understand its capability. Most new PC enthusiasts use brand names and budget-specific processors to fulfill their needs. However, due to the increasing number of Intel CPUs, it’s a good idea to use a naming scheme with its new Intel Core Ultra rebranding.
Intel ditched the ‘i’ prefix from its top-tier Core Ultra processors to make a simple naming lineup. However, these suffixes, SKUs, and letters in the new naming convention aren’t easy to remember. As a result, some people end up buying a processor that may not be entirely suitable for their usage. We expect Intel will come up with an easier way to do it.